Acids Bases and Salts: Class 7 Science NCERT Chapter 5
Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 – Acids,...

In the previous chapter: Human Health and diseases you studied what are diseases and some common diseases in humans. In chapter 9 of Class 12 NCERT Biology book: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production, you will learn about the developing total population is joined by numerous issues, the most significant being a lack of food materials. Researchers everywhere throughout the world are occupied with discovering new techniques for upgrading food creation. One center in regards to this is animal husbandry. Let us study more about it.
To satisfy the interest of food things because of expanding populace, natural standards are applied in animal husbandry and plant breeding.
It is the farming act of reproducing and raising domesticated animals. Animal husbandry manages the care and reproducing of animals like cows, buffalos, pigs, cattle, horses, sheep, camel goat and so on. It incorporates poultry farming and fisheries. Fisheries incorporate raising, obtaining, selling, and so forth., of fish, molluscs (shell-fish) and crustaceans(prawns, crabs, and so on.) More than 70% of domesticated animals populace of the animals live in India and China.
An expert methodology of ranch management has expanded food creation in many folds. Some of the management systems applied in different domesticated animals are as per the following-
Dairying is the management of creatures for its milk and its item for human utilization. In dairy farm management, we conduct procedures and systems that increase yield and improve the nature of milk.
Poultry is the kind of trained birds utilized for food or for their eggs. It primarily incorporates chicken and ducks, turkey and geese. Significant components of poultry farm management incorporate:
It targets growing yields of creatures and improving the alluring characteristics of the item. A breed is a gathering of creatures related by descent and similar in the majority of characters like general appearance, configuration, features, size, and so forth. There are two sorts of rearing

Persisted inbreeding diminishes fertility and even efficiency. This is called Inbreeding Depression. At whatever point this turns into an issue, chose creatures of the reproducing populace should be mated with superior creatures of a similar variety. This generally reestablishes fertility and yield.
The rearing of unrelated creatures, which might be between individuals of the same kind, in any case, having no common ancestors or between different breeds (cross-breeding) or different species (interspecific hybridisation) is outbreeding.
Out-crossing this is the act of mating of creatures inside a similar variety however having no common predecessors on either side of their family up to 4-6 age. The offspring are known as out-cross.
The superior male of one breed is mated with a predominant female of another kind. Crossbreeding permits the attractive characteristics of two breeds to be consolidated.
Interspecific hybridisation-
male and female creatures of two unique species are mated. The descendants may consolidate attractive highlights of both and parents. Ex-donkey.
Controlled breeding examinations are done utilizing manual semen injection. The semen is gathered from the male that is picked as a parent and infused into a conceptive lot of the chose female by the breeder.
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) is utilized to build the achievement rate of planned impregnation. In this strategy, a dairy animal has administrated hormones (FSH) to actuate follicular development and superovulation, rather than one egg; they produce 6-8 eggs. The fertilized eggs 8-32 cells stages, are recouped non-surgically and moved to surrogate mothers. The hereditary mother is accessible for another round of superovulation.
Bee-keeping or apiculture is the care of hives of bumblebees for the creation of honey. Honey is a food of high nutritive quality and furthermore discovers use in the indigenous system of medicine. It additionally delivers beeswax.
The most widely recognized types of Honey bee is Apis indica. Below are the points that are significant for effective honey beekeeping-
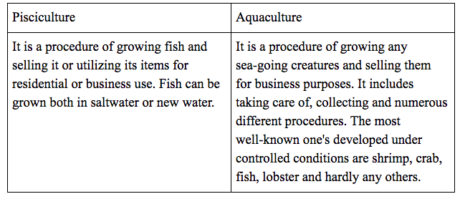
The fishery is an industry dedicated to catching, preparing or selling of fish, shellfish or other sea-going creatures.
New water fishes which are regular incorporate catla, rohu and common carp. Common marine fishes are Hilsa, mackerel, sardines and pomfrets.
Various strategies have been applied to improve production like aquaculture and pisciculture. Blue Revolution is executed to expand fish creation.
Plant Breeding is the deliberate control of plant species so as to make wanted plant types that are more qualified for development, give better yields and are ailment safe.
Classical plant reproducing includes crossing or hybridisation of pure lines, trailed by counterfeit choice to deliver plants with alluring attributes of better yield, nourishment and protection from illness.
a) Collection of variability is the assortment and protection of all the diverse wild varieties, species and family members of the grown species. The whole collection having all the various alleles for all qualities in a given yield is called germplasm collection.
b) Evaluation and determination of guardians is the identification of plants with an alluring mix of characters. The chosen plants are multiplied and utilized during hybridisation.
c) Cross hybridisation among the chosen parents to acquired wanted yield characters for instance high protein nature of one parent may need to be joined with disease restraint from another parent. This is conceivable by cross hybridizing the two parents to create crossovers that hereditarily join the ideal characters in a single plant
d) Selection and testing of superior recombinants: The determination procedure is significant to the accomplishment of the reproducing objective and requires a cautious scientific assessment of the offspring. This step yields plants that are better than both of the parents.
e) Testing, removing and commercialisation of new crops: The recently chosen lines are assessed for their yield and other agronomic characteristics of value, illness obstruction, and so on.
Production of wheat and rice expanded colossally between 1960-2000 because of presentation of semi-dwarf assortments of rice and wheat.
Saccharum Barberi and Saccharum officinarum were crossed to get the attractive characteristics of high return, thick stems, high sugar and capacity to develop in the sugar cane regions of north India.
Hybrid maize, jowar and bajraare produced in India. These assortments are high yielding and impervious to water pressure. Plant Breeding for Disease Resistance
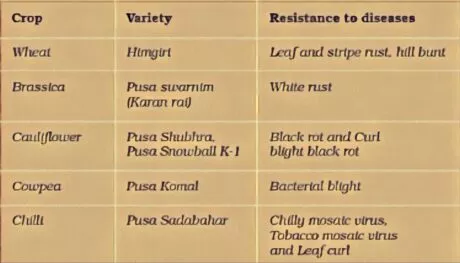
A few contagious, bacterial and viral microorganisms influence the yield and nature of plant items. To limit this misfortune disease resistance varieties were created. Reproducing is done by customary strategy or by mutation rearing.
Some crop assortments reproduced by hybridisation and determination for disease resistance from parasites, bacterial and viral malady are released
The mutation is the procedure by which hereditary varieties are made through changes in the base arrangement within genes bringing about the creation of another character or trait not found in the parental kinds. It is done by utilizing mutants like chemicals or radiations. This procedure is called mutation reproducing. e.g
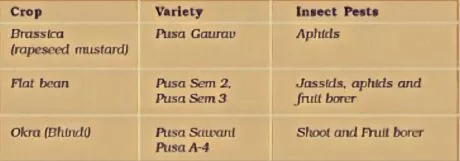
Harvest plant and yield items are destroyed by insects and pets on a huge scale. To forestall this misfortune new assortments resistance from them are created.
Bio-fortification Breeding crops with more elevated levels of nutrients and minerals, or higher protein and more beneficial fats. Breeding for improved healthful characteristics have following targets of improving
Atlas, 66, having a high protein content, has been utilized as a benefactor for improving grown wheat.
IARI, New Delhi has discharged numerous varieties of vegetable crops rich in vitamins and minerals. An improved, spinach, carrot, and pumpkin and vitamin C enriched bitter guard, bathua, mustard, iron and calcium enhanced spinach and; protein improved beans: wide, lablab, French and garden peas.
Another source of protein for the creature and human sustenance. Organisms are developed on a mechanical scale as a source of good protein.
The ability to produce entire plants structure any cell/explant is called totipotency. Many plants can be delivered from explants in short time frame utilizing reasonable nutrient medium, aseptic condition and utilization of phytohormones. This strategy for creating a large number of the plant is called micropropagation. Each of these plants will be hereditarily indistinguishable from the first plant from which they were developed, i.e., they are someaclones. Numerous significant food plants like tomato, banana, apple.
the recovery of healthy plants from ailing plants should be possible by meristem culture. Although the plant is contaminated with an infection, the meristem (apical and axillary) is liberated from infection. Henceforth, one can evacuate the meristem and develop it in vitro to get infection-free plants
Separation of single cells from their plants and after digesting their cell wall fusing the cytoplasms of two different assortments is called somatic hybridisation and these hybrids are called somatic hybrids.
State the reason why are interspecific crosses uncommon in nature and intergeneric almost unknown?
Ans. Interbreeding is a significant criterion for individuals from any species. In the event that two people can’t breed, they can’t be termed to have a place with similar animal varieties. Subsequently, interspecific crosses are uncommon in nature. Some rationale applies to intergeneric crosses.
The fundamental explanation lies in the distinction in the number of chromosomes in the cells of various living beings. Because of this, a feasible zygote can’t be shaped by two gametes having various quantities of chromosomes. In any case, fake hybridization is by frequently utilised to create interspecific and intergeneric crosses; particularly for delivering better varieties of plants.
0 responses on "Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Class 12 Biology NCERT Chapter 9"