Acids Bases and Salts: Class 7 Science NCERT Chapter 5
Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 – Acids,...

In the previous Chapter 13: Fun with magnets of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science you studied the invention and working of magnets In this chapter of NCERT class 6 Science: Water, you will learn about how water is a significant element needed to nourish life on earth.
It is the dissemination of water through the procedure of vanishing or buildup as a downpour or snowfall. The water cycle resembles a ring. In nature, the water cycle happens from the ocean to land and back to the ocean once more.

The water that falls on the land as downpour and snow at some point or another returns to seas. This may occur from various perspectives.
Streams and springs: Most of the water which people use for drinking, washing, and cultivating originates from waterways and springs. The stream streams down the mountainside and over the land, at long last streaming into an ocean or a sea.
Seas and oceans: Most of the water on the earth is found in the seas and oceans. Notwithstanding, the water found in the seas and oceans isn’t good for drinking or agrarian purposes as it contains an enormous measure of salt. Notwithstanding, the sea goes about as a living space for a huge number of plants and creatures.
Day off: areas of the earth is secured with snow particularly during winters. Water shaped by dissolving of snow is another wellspring of water. This snow dissolves gradually. In some cases, this water streams down as streams and waterways. Streams and waterways are other wellsprings of water.
Groundwater: The groundwater is really rainwater which originates from the drainage of water aggregated under the ground. Figure 14.3 shows the gathering of groundwater.
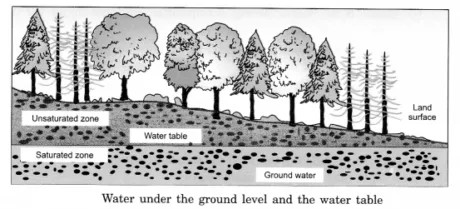
Water table: If you take soil from the ground, it has air just as water. As you go down, the measure of water increments and air diminishes. A level underneath the surface, where it is just water, is known as the water table.
Lakes: These are little supplies of water. These are made by the Collection of rainwater in low lying zones. Drainage from the groundwater saves additionally adds to the water in lakes and lakes.
Downpour: The downpour is a significant wellspring of water for us. All assets of water are taken care of for the most part by downpours.
Dry season: If it doesn’t rain for a year or more at a spot, the dirt will lose its water by dissipation and gets dry. Water will likewise be lost through the transpiration process from the plants. Waterways, lakes, and wells will dry and the water table would dropdown. This will influence people, creatures, and wild plants. If it proceeds for a couple of years sequentially, it results in the dry season.
Outcomes of draughts: The consequence of draughts might lead to no farming. The accessibility of food and water will diminish. The general result of such a circumstance will prompt the death toll of people and creatures to rise.
Flood: if there should be an occurrence of constant rains, the water level of waterways, lakes, and lakes will rise. The dirt surface will get weighed down with water coming about into flood. Outcomes of the flood: When the soil gets a lot of water, the air in the soil comes out. Because of the absence of air, the creatures living inside the dirt likewise come out of it. Substantial rainfall likewise brings about the loss of harvests because of the flood.
Significantly, water ought to be utilized cautiously. We should take care that water ought not to get squandered.
It isn’t fundamental that the water utilized in the nursery is good for drinking. However regularly we water the nurseries with drinking water provided by the enterprise. We should utilize water for planting that has just been utilized in the kitchen for washing vegetables and organic products, and so on.
Be careful that the water tank in your home doesn’t flood when it is being filled.
Try not to utilize a hose channel to wash your vehicle or bike. Utilize a bucket.
In case you leave the tap running while at the same time brushing your teeth, around 16 litres of water gets spent. Fill a mug with water and use instead.
Water gathering is the action of an assortment of water straightforwardly by different methods.
Collected water can either be utilized promptly or it very well may be put away for some time in the future.
In Kerala and Mizoram, where it rains nearly the entire all year, little tanks are utilized to gather water, which channels from housetops through funnels into these tanks. This water is utilized legitimately.
In a spot like Delhi where the rain keeps going just for 3 months, it is progressively helpful to gather water as groundwater.
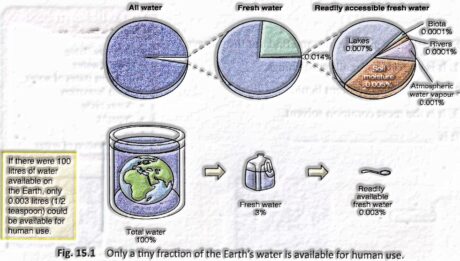
Around three-fourths of the Earth’s surface is secured with water. That is the reason it is likewise called the water planet. However, do you realize how much water is promptly accessible for use? A large portion of the water (about 97%) is in the oceans and seas as saltwater. This water is too pungent to be in any way utilized for drinking and water system. In this way, just a little division (about 3%) of the Earth’s water is accessible to us as freshwater. Out of this, 2.997% is secured up in the mountains or ice sheets or is covered so profound under that it is too expensive to even think about extracting.
In this way, just about 0.003% of the new water is effectively accessible to us as groundwater, waterway, lake, stream, soil dampness, and water fume. See Figure 15.1.
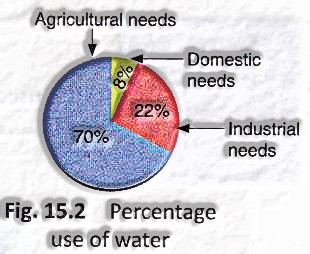
Other than being basic forever, water is utilized for some different purposes. In India, about 70% of the complete water accessible is utilized for agribusiness, 20-22% by businesses and just 8% is utilized for individual or household needs. Figure 15.2 shows a pie diagram that gives the rate utilization of water.
Let us get familiar with the different employments of water.
Farming needs Our nation relies a ton upon agribusiness. Ranchers depend on water to continue their farming yields, e.g., wheat, paddy, and so forth. Commonly, precipitation isn’t adequate to water these harvests, and ranchers need to utilize counterfeit watering frameworks, alluded to as a water system.

Mechanical requirements Factories utilize a lot of water each day—as crude material, for cleaning, warming, cooling, producing power (e.g., water turbines), and so forth. The measure of required relies upon the sort and size of the plant, and water.
Individual/residential requirements: We need water to drink. Water that is reasonable for drinking is called consumable water. We likewise need water to wash, wash garments and dishes, clean our home, and to water plants.
Aside from these utilizations, water is additionally utilized for transportation and diversion (Fig. 15.6). It additionally directs the atmosphere of a spot and gives homes to numerous creatures.

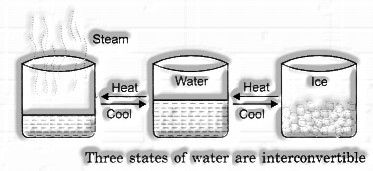
In nature, water exists in three states. It could be as fluid (e.g., rain, waterway, ocean), strong (e.g., ice, a day off), or gas (e.g., water fume) (Fig. 15.7).
You can warm water over an oven to change over it into fume. What occurs on the off chance that you leave water in a revealed vessel on a late spring evening outside your home? Following a couple of hours, you will find that the degree of water in the vessel has diminished. This is because a great deal of it would have gotten away into the air as water fume. The procedure by which a fluid is changed over to its fume is called evaporation.
Shouldn’t something be said about the converse procedure? The procedure by which the fume of a substance is changed over to its liquid form is called buildup. Water fume is likewise included in the air by the leaves of plants, through the procedure of transpiration.
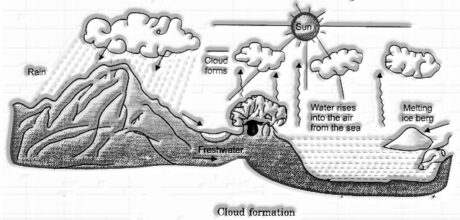
Evaporation and buildup of water happen on an extremely huge scope on the outside of the Earth and its climate. These procedures assume a key job in cloud forming and rain.

At the point when the temperature of air builds, it extends (i.e., its particles move away from each other). This makes the air lighter and it ascends in the environment, taking water fume with it. As the air rises, it starts to cool. The water fume consolidates on dust particles present in the environment to frame a great many small beads. Minuscule ice precious stones will be framed rather if it is freezing. This group of small water beads coasting noticeable all around is the thing that we call a cloud.
Water Cycle
Water beads in the mists continue knocking against each other and here and there stick to shape greater drops. At the point when these drops become too overwhelming to even consider floating noticeably all around, they drop down back to the Earth as rain. The water that descends as rain, in time, dissipates and goes up to frame mists once more. This prompts framing a cycle, known as the water cycle.
The water cycle is the cyclic development of water from the environment to the Earth and back to the climate through different procedures.
Figure 15.9 shows how the water cycle functions.
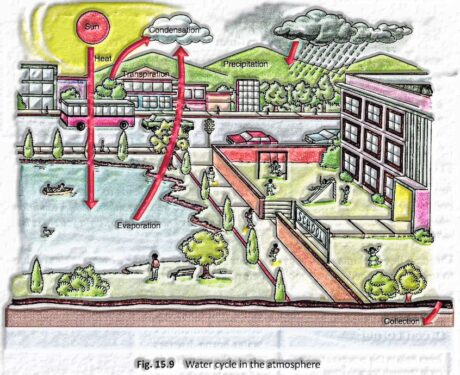
Evaporation Sun’s warmth changes the water in seas, waterways, lakes, and other water bodies into water fume. Transpiration Plants radiate water fume through their leaves.
Buildup Water fume ascends and consolidates on dust particles to frame mists.
Precipitation Water put away in mists arrives at Earth as rain, a day off.
Assortment Some rainwater saturates the ground, shaping groundwater. Rainwater additionally streams into streams and waterways and afterward discovers its way into oceans and seas.
Some of the time it doesn’t rain for quite a while—for a whole month, two months, the entire season, two years, and so forth. The anomalous significant stretch of lacking or no rainfall at all is called drought. During drought, streams run dry, the water level in lakes goes down, and even the water in the dirt evaporates (Fig. 15.10).
There is almost no or no water accessible during a drought. Most amazing to an absence of food in the area. The absence of food in a locale for a significant stretch is called starvation. When there are no plants, creatures that make due on plants additionally bite the dust. Creatures and people likewise pass on because of thirst and drying out (exorbitant loss of water from the body).

Similarly, as too little rain is terrible, an excessive amount of rain is awful also. It prompts water being all over, now and then the whole zone stays submerged or lowered. A condition when the ground gets lowered submerged, because of substantial rain and flooding of streams is called a flood.
During a flood, plants and harvests pass on either because of suffocation by abundance water or because of the dirt being washed away, ransacking their underlying foundations of help.
In such waterlogged conditions, numerous illness-causing germs begin duplicating and cause water-borne infections. In some cases, water-borne ailments influence a huge number of individuals simultaneously. An ailment influencing a great many individuals simultaneously is called an epidemic.
A flood would thus be able to prompt numerous conditions—ailment, starvation, death toll, and property. A flood additionally can have a similar impact on the evolved way of life as a drought does.
Both drought and flood are cataclysmic events—terrible occasions achieved essentially—that can have a solid impact on the lives of individuals. The economy of a nation can disintegrate because of the loss of property and life and a lot more things. Be that as it may, we can and should attempt to diminish the terrible impacts of these debacles however much as could reasonably be expected. We should comprehend that such things can occur, thus we should be set up to confront them as and when they occur.

Since just a little level of water on our planet is usable, it is significant that we use water cautiously. Preservation of water should be possible by building dams, keeping away from wastage of water at homes, both inside and outside, gathering rainwater, and forestalling contamination of water.
A dam is a structure worked to keep down water to forestall floods and to give water to irrigation and capacity.
Building a dam is an answer for both drought and flood (Fig. 15.12).
Dams are likewise utilized in creating power. Based on waterways, a dam has high dividers and has numerous openings or entryways to both lets in and keep down water.
During overwhelming precipitation, when the waterways top off, water enters the dam. At the point when water is required later, the entryways are opened to let out water.

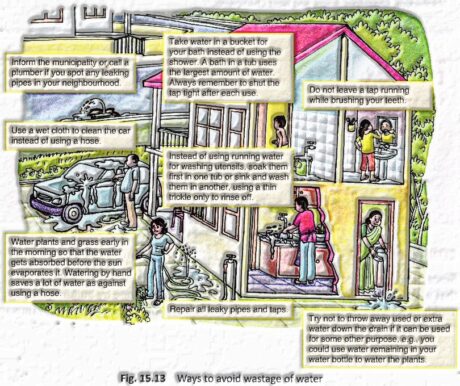
A few different ways to stay away from wastage of water at homes are given underneath.
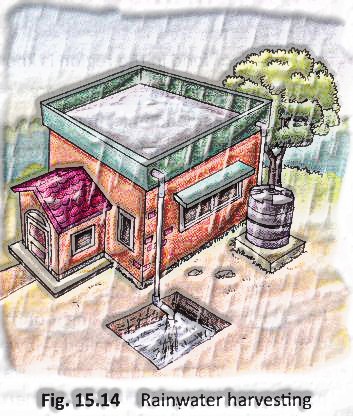
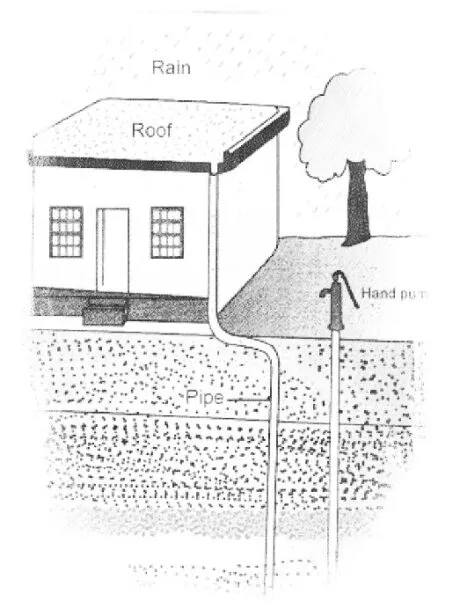
The way toward gathering and putting away rainwater from rooftops or a surface catchment is called rainwater harvesting (fig. 15.14). Putting away rainwater that gathers on rooftops as opposed to releasing it down the channel, is a useful arrangement in the event of droughts. This procedure is known as housetop rainwater harvesting. This includes gathering rainwater from housetops in burrow lakes, vessels, or underground tanks to store water for extensive stretches. Another alternative is to permit water to go into the ground legitimately from the side of the road depletes that gather rainwater. The put-away rainwater is treated before use since it might contain feathered creature defecation, synthetic compounds, and different poisons, which should be evacuated before use.

Another technique to ration water is to protect our freshwater bodies from contamination. Trash and destructive synthetic compounds dirty the water and make it ill-suited for use. Dirtied water (Fig. 15.15) is likewise terrible for sea-going life. Plants and creatures in and around dirtied water may pass on or get tainted. Furthermore, when people devour polluted fish, and so forth., they are likewise put in danger of maladies.
The water of the oceans and seas that has high salt substance, making it unsuitable for drinking and irrigation, is called saltwater.
Water found in waterways, lakes, and lakes utilized for household and business reasons for existing is called new water.
Watering crops by counterfeit methods is called irrigation.
Water fit for human utilization is called potable water.
The arrival of water fume into the environment through the leaves of plants is called transpiration.
The cyclic development of water from the environment to the Earth and back to the climate through different procedures is known as the water cycle.
An abnormally significant stretch of deficient or no precipitation is called drought.
Lack of food in a locale for a significant stretch is called famine.
A condition when the ground gets lowered submerged, because of substantial downpour and flooding of waterways is called a flood.
An ailment influencing a large number of individuals simultaneously is called an epidemic.
A structure based on a stream to store and keep down water is known as a dam.
The way toward gathering and putting away rainwater from rooftops or a surface catchment is called rainwater harvesting.
Just a minuscule portion of the Earth’s water is accessible as new water. Every single living thing has a great deal of water in their body. Practically 70% of our body weight contains water.
We need water for some, reasons—drinking, individual needs, rural necessities, mechanical requirements, transportation and entertainment, and directing the atmosphere. It is home to different plants and creatures.
Water exists in strong, fluid, and vaporous states.
Dissipation and buildup assume a significant job in cloud development.
The water cycle is the cyclic development of water from the climate to the Earth and back to the air through different procedures.
The strangely extensive stretch of deficient or no precipitation is known as drought.
When there is an excess of precipitation in a zone, waterways flood and water spread all the zone around. This is known as a flood. A flood can cause extraordinary pulverization.
Rainwater harvesting is one of the approaches to save water.
0 responses on "Water: Class 6 Science NCERT Chapter 14"