Natural Vegetation and Wildlife:Class 9 Geography NCERT Chapter 5

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 9 Geography Chapter 5 – Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
In the previous Chapter 4:Climate we have learned about the factors affecting our climate in the country.In this chapter 5:Natural vegetation and wildlife we will study our country’s natural vegetation and wildlife.
Quick revision notes
India is one of the twelve mega bio-assorted variety nations of the world. They are a gathering of nations that have most of the Earth’s species and along these lines, considered very bio-differing.
Being a huge nation, India having 47,000 plant species (out of which 15,000 are blossoming plants, for example 6 percent on the planet), involves tenth position worldwide and fourth in Asia. Non-blossoming plants, for example, greeneries, green growth and organisms additionally develop here. It likewise has around 90,000 types of creatures (counting marine and water fishes) and creepy crawlies.
Natural Vegetation
Natural or virgin vegetation implies the plant network which has developed normally with no human mediation for quite a while. That common vegetation, which are left undisturbed over an extensive stretch of time are called virgin vegetation.
Natural vegetation are of two kinds
- Endemic species Those plant species which began from the nation, are named as endemic species.
- Fascinating species Those plant species which started outside the nation are named as extraordinary species.
Elements Affecting Diversity
Components which impact the assortment of verdure incorporate Relief (land and soil), Climate (temperature, photoperiod and precipitation) and the Ecosystem. These are as per the following
Help
It incorporates land and soil.
Land
It influences the normal vegetation both legitimately and in a roundabout way. The idea of the land for example regardless of whether it is plain, uneven or a level, decides the sort of vegetation which will develop in it. Ripe terrains are utilized for developing yields, vegetables and natural products.
Undulating (Wavy) and harsh surfaces for the most part form either into fields or forests (backwoods). Various sorts of land likewise continue and give asylum to various types of untamed life.
Soil
The dirts likewise change all around. Various types of soils give various types of vegetation. For instance, alluvial or deltaic soil of a waterway delta close to the ocean will continue mangrove timberlands while inclines of slopes have conelike trees. The sandy soils of desert continue prickly brambles.
Note Animals and feathered creatures likewise occupy areas dependent on alleviation. For instance, transitory fowls like the Siberian cranes and flamingoes are found to settle in the wetlands of the Rann of Kuchchh, where the desert converges with the ocean.
Atmosphere
It incorporates temperature, photoperiod and precipitation.
Temperature
The temperature alongside the stickiness noticeable all around and precipitation decide the character of vegetation and its degree.
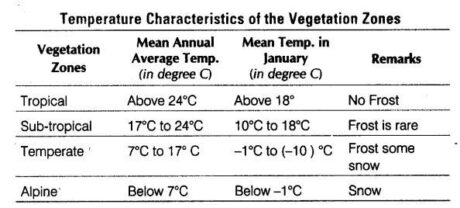
As the atmosphere gets colder, either by increment in height (above 915m) or by disappearing from the equator, the vegetation will change from tropical to sub-tropical, mild and afterward high.
For instance, on the slants of the Himalayas and slopes of the Peninsula, the fall in temperature influences the kind of vegetation and its development
. 
Photoperiod (Sunlight)
The sum and span of daylight is known as photoperiod. The distinction in scope, elevation and season gets variety span of daylight in better places. In hotter locales and atmospheres, plant development is quicker because of longer term of daylight, particularly with accessibility of satisfactory dampness. An example is the way that the Southern slants of the Himalayas are secured with thicker vegetation than the Northern inclines.
Precipitation
Propelling South-West rainstorm (June to September) and withdrawing North-East (October-November) storms bring practically all the precipitation in India. Territories of weighty precipitation consistently have denser vegetation than different zones with lesser precipitation. The South-West storm downpours on the windward side of the Western Ghats, accordingly cause a weighty development of tropical evergreen timberlands there, though the leeward side doesn’t have any such woods.
Environment
Different types of plants happen in regions having comparative climatic conditions. To a huge degree its inclination decides the creature life around there. All the plants and creatures in a zone are associated on one another in their physical condition and structure an environment.
Accordingly, a biological system is a natural domain comprising of the apparent multitude of life forms living in a specific territory, just as all the non-living, physical parts of the earth with which the creatures associate, for example, air, soil, water and daylight.
Biome
It is a significant network of plants and creatures having comparable living things existing under comparable natural conditions. A biome is distinguished based on plant existing there. It is additionally named as ‘significant life zone’.
Backwoods are sustainable assets and assume significant job in upgrading nature of Environment.
Summary
The vast majority of India’s regular vegetation are found in Himalayas, sloping districts of focal India and in desert.
Biomes are enormous biological system ashore and have particular kinds of vegetation and creature life.
Significant vegetation types distinguished in India are tropical evergreen backwoods, tropical deciduous woods, tropical thistle woodland and scours, montane timberlands and Mangrove timberlands.
Tropical Evergreen woodland is found in locale of high precipitation.
Tropical deciduous backwoods or storm woodlands are the most far reaching timberlands of India.
The thistle backwoods and scours are found in locale with less that 70 cm precipitation.
Montane woodlands are high height elevated vegetation.
Mangroves are flowing vegetation found along the waterfront area. Sundari is a significant mangrove tree.
The World Conservation Union distributes Red rundown of fundamentally undermined and imperiled plant species.
India has 13% of the world’s absolute fowl species and 12% fish stocks.
The Wildlife Protection Act in India was executed in 1992.
The exorbitant misuse of the plants and creature assets by Human creatures drove them to get imperiled and wiped out.
Chasing, contamination, the presentation of outsider plant and creature species, deforestation are significant dangers for the environment.
Administration of India has found a way to ensure plant and creatures, for example, – setting up of public parks, biosphere holds and so forth, the acquaintance of various activities with ration basically imperiled species for example venture tiger, venture rhino and so on.
We as a whole ought to know about the way that a characteristic environment is significant for our endurance.

