Climate:Class 9 Geography NCERT Chapter 4

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 – Climate
In the previous Chapter 3:Drainage we have learned about different water bodies and some major rivers flows in our country.In these Chapter 4:Climate we will study about the factors affecting our climate in the country.
Quick revision notes
The term climate is the whole of.the climate conditions (counting varieties) over an enormous zone for a significant stretch of time (over thirty years).
The term climate alludes to the condition of the air at a spot and time concerning the accompanying components
- Temperature Humidity
- Pneumatic force
- Darkness or daylight
- Precipitation (Rainfall or snowfall)
- Wind
The climate conditions change frequently inside a day. In light of the summed up fhonthly environmental conditions, the year is separated into seasons, for example, winter, summer and stormy seasons. The world is separated into various climatic districts. In Asia, India and other South and South-Eastern nations have storm sort of climate.
The word storm is gotten from the Arabic word ‘mausim’ which actually implies season. ‘Storm’ alludes to the occasional inversion in the breeze heading during a year.
Territorial Climatic Variation In India
Despite the fact that there is a general solidarity in the overall climatic example in India, there are some detectable territorial varieties.
Temperature
The temperature in the winter in North-Western rugged locales can go down to – 45° C (at Drass in Jammu and Kashmir), while it is 22°C in Thiruvananthapuram in Kerala. So also, it can go up to 50°C in summer in certain pieces of Western Rajasthan and 20°C in Shillong.
In numerous zones, there is a wide variety among day and night temperatures. In the Thar Desert, the day temperature may ascend to 50°C and drop down to approach 15°C the exact night. Then again, there is not really any distinction in day and night temperatures in the Andaman and Nicobar islands or in Kerala.
Precipitation
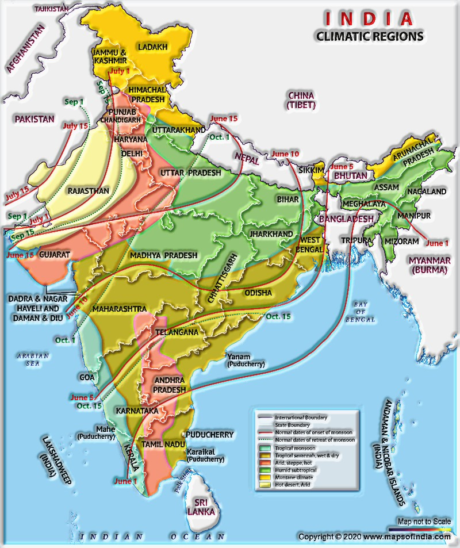
There is a wide variety seen in its sum and occasional dissemination. Precipitation as snowfall happens just in upper pieces of Himalayas, the remainder of the nation gets precipitation.
A regular model, the yearly precipitation differs from more than 400 cm in Meghalaya to under 10 cm in Ladakh and Western Rajasthan. Essentially, most pieces of the nation get precipitation from June to September, however the Tamil Nadu coast gets the vast majority of its downpour during October and November.
Waterfront locales experience diverse climate conditions from the inside areas. For instance, temperature and occasional differentiation are moderately gentle. The precipitation likewise diminishes from East to West. Such contrasts help to make an assortment in lives of individuals—the food they eat, the garments they wear, the sort of houses they utilized for living, etc.
Elements Affecting India’s Climatic
Scope
The Tropic of Cancer (23°3 CV N) isolates the nation into the tropical zone (South of this line) and the sub-tropical zone (North of this line). The line runs from the.Rann of Kuchchh (West) to Mizoram (East). All the rest of the zone, North of Tropic, lies in sub-tropics. Along these lines, India’s climate has qualities of tropical just as sub-tropical climates.
Elevation
Mountains-in the North of India have a normal height of around 6000 m, though on the seaside territories just as islands, most extreme rise is around 30 m.
The Indian sub-landmass encounters milder winters when contrasted with Central Asia due to the Himalayas which keep the virus twists from entering the sub-mainland.
Weight and Winds
The accompanying air conditions oversee the climate and related climate conditions in India
- Weight and surface breezes
- Upper air course
- Western cyclonic aggravations and tropical tornadoes
Summary
Climate is the aggregate of the climate conditions and varieties over an enormous territory for a significant stretch of time, by and large over 30 years.
Climate is the condition of the air over a territory anytime of time.
Different components of climate and climate are temperature, environmental weight, wind, moistness and precipitation.
India alongside South and South-East Asia has storm kind of climate.
The climate of wherever is constrained by scope, height, weight and wind framework, good ways from the ocean, sea flows and help highlights.
High mountain by hindering the downpour bearing breezes helps in causing precipitation in windward side of mountain.
The air conditions which administer the climate and climate state of India are-weight and surface breezes, upper air flow, western cyclonic unsettling influences and tropical tornado.
Coriolis power which is created by the turn of the earth is answerable for diverting breezes towards the privilege in Northern half of the globe and towards the left in Southern side of the equator.
South-West rainstorm winds are South-East exchange winds of Southern half of the globe which in the wake of intersection equator, become South-Western exchange twists (due to rightward diversion by Coriolis power). As they blow over warm sea, they cause precipitation in Indian sub-landmass.
Fly streams are quick blowing breezes moving in the upper air. They are situated at about 27°-30° North scope.
Shallow cyclonic sorrows beginning over the Mediterranean sea are known as Western aggravations. They cause winter precipitation in-North Western pieces of India.
Rainstorm is gotten from Arabic word ‘Mausim’. It alludes to the reasonal inversion in wind course consistently.
The Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a wide trough of low weight in central scope. In ITCZ, there is union of North-east and South-East exchange wind.
Southern Oscillation (SO) is the inversion of weight conditions and the other way around in Southern Pacific sea and Eastern Indian sea.
ENSO is the blend of EL Nino and Southern Oscillation. The adjustments in pressure conditions are associated with EL Nino, henceforth, the marvel is alluded to as ENSO.
The rainstorm trough is the extreme and lengthened low-pressure territory, which creates over North-Western India. It stretches out from the Thar Desert in West to Chota Nagpur level in East.
The pre-rainstorm shower in seaside Karnataka and Kerala is called Mango shower. It helps in early maturing of Mangoes.
The sweltering and damp condition which makes the climate severe is called October heat. It happens towards the finish of withdrawing rainstorm in the long stretch of October.
With a musical pattern of seasons, wherein individuals celebrate numerous celebrations and do different exercises, the rainstorm joins the Indian sub-mainland and goes about bringing security together.

