Body Movements:Class 6 Science NCERT Chapter 8

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 6 Science Chapter 8 – Body Movements
In the previous chapter 7: Getting to know plants where we have studied about the plants and the function of its parts.In this chapter 8: Body movements we will study about the function of body parts which helps in our movements.
Quick revision notes
Skeletal System
- Bones in our body structure is the system that bolsters the entire body. This system is known as the skeleton.
- Our skeleton is comprised of various bones and ligaments.
- There are around 650 muscles joined to the different bones in our body.
- The bones are hard and inflexible.
- Cartilages are nearly delicate and flexible.
Functions of skeleton
- Skeleton framework offers backing to the body.
- It ensures the internal organs.
- Along with muscles, it gives the body its shape.
- Red platelets and some white platelets are created in the marrow of the bone.
X-ray machine: We can get photos of bones by a machine called x-ray machine. Specialists utilize these photos to inspect the wounds and infections of bones.
The bones in our body fluctuate in their sizes and shapes. Various kinds of c bones have various capacities.
The skull: The skull has two primary parts:
- Cranium: The bones of Cranium are the same level. They are held solidly like a zipper. It covers and secures the mind.
- Facial bones: The facial bones include the upper jaw, lower jaw and hardly any different bones. The lower jaw is versatile. The development of lower jaw empowers us to eat, talk and sing.
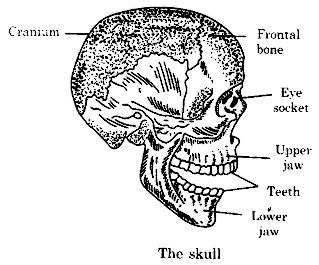
Eye sockets: The skull additionally incorporates a couple of eye attachments. These structure a sheltered pocket for eyes.
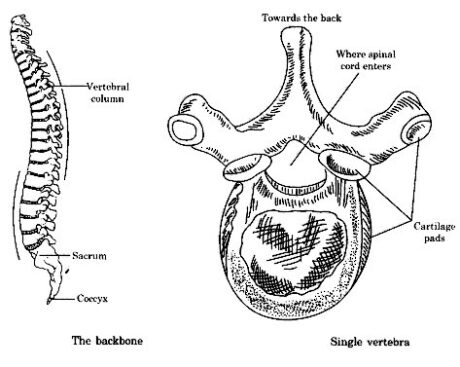
The backbone: Backbone or vertebral section is made out of 33 little, ring like vertebrae joined start to finish. It frames an empty hard cylinder. The principle nerve rope goes through it.
The Chest bones: 12 sets of ribs alongside spine make a cone-formed pen, called rib-confine, which secures the heart.
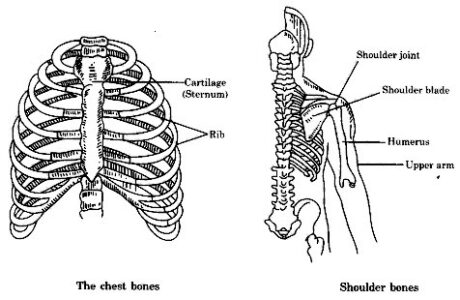
The Shoulder bones: The shoulder bone is shaped by the collor bone and the shoulder bone. The shoulder bones are level and huge. They help in shaping joints with long bones.
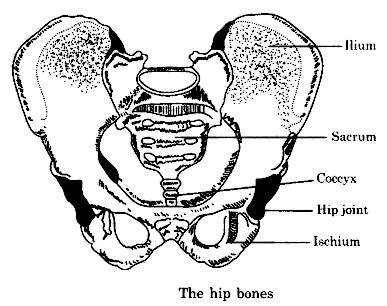
Hip bones: The hip bone is framed by the combination of three bones. Like shoulder bones, the hip bones are additionally level and enormous. They help in framing joints with long bones. Along with the last two pieces of spine, it shapes a huge hard bowl called pelvis.
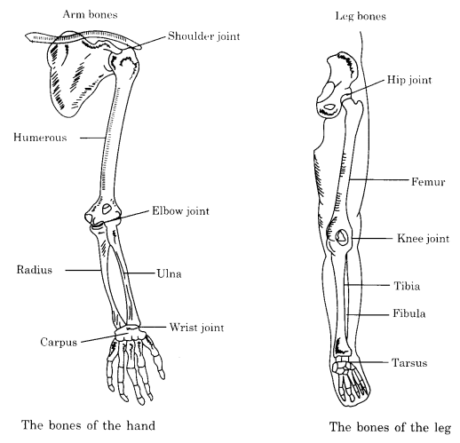
Bones of hands and legs: Bones of arms, thighs, and so on., are long. They invigorate our body. Bones of fingers and toes are short. They help us in holding things. The hands and legs are developed in same example as portrayed beneath: (See Figs).
| Part of hand | Part of leg | Number of Bones |
| Upper arm | Thigh | One long bone |
| Fore arm | Lower leg | Two long bones |
| Wrist | Ankle | Several small bones |
| Palm | Foot | Five bones |
| Fingers | Toe | Each has three small bones besides the thumb, with two small leaves) |
Bone joints: where at least two bones get together is known as a joint. In our body, five kinds of joints are available to be specific:
- Fixed joints which don’t permit development, e.g., joints of the noggin.
- Ball and socket joint permit development every which way, e.g., joints between upper arm and shoulder, thigh and hip.
- Pivotal joint permit development just one way, e.g., fingers, the knee, and so on.
- Hinge joints permit movement in just one way, e.g., fingers, the knee, and so on.
- Gliding joints permit just a constrained measure of development, e.g., joints of the spine.
Muscles: The bones are handled by the alternate contractions and relaxations of two sets of muscles.
Tendons: join muscles to the bones.
Ligament: joins two bones.
Bristles: Bristles are hair like structure, associated with muscles. The fibers help to get a decent grasp on the ground. ‘
Cavity: It is the empty space or hole in one bone, into which the other bone fits. Such joint permits developments every which way.
Gait of animals: Some creatures don’t have bones. They have muscles which help to broaden and abbreviate the body. During development, creature initially broadens the forward portion of the body, keeping the back position fixed to the ground. After that creature fixes the front end and discharges the backside. Presently creature abbreviates the body and pulls the backside forward. During this training, creature pushes ahead by a little separation.
Rib cage: Ribs get together with the chest bone and the spine together to frame a container. This is called rib confine.
(Chapter 8: Body movements)
Locomotion
There are two sorts of developments:
- The creatures move their body parts without changing their position.
- Creatures move to start with one spot then onto the next. This sort of development is called headway.
Locomotion in some Animals
- Birds
A large portion of the winged animals have two sorts of headway. They stroll with legs on the ground. They additionally fly noticeable all around. Ducks and swans likewise swim in water. - Flying adaptations: Streamlined body, bones with air spaces, forelimbs changed into wings, air sacs associated with lungs and enormous flight muscles are a few adjustments in flying creatures for flying.
- Fish: The fish swims by shaping circles on the other hand on the different sides of the body. The tail pushes them forward. The vertebrae and the muscles connected to them work for it.
- Snakes: Similarly, the snakes slither on the ground by on the other hand circling sideways. An enormous number of vertebrae and related muscles push the body forward. The ventral scales likewise help all the while.
- Insects: The body and legs of insects have hard joined covers, framing an exoskeleton. The muscles of the bosom associated with three sets of legs and two sets of wings help the cockroach to walk and fly.
- Snails: The snails are moved by the solid foot. The hard unjoined shell have no connection with the foot.
- Earthworm: The earthworm moves by interchange augmentation and constriction of the body influenced by the muscles. The moment versatile fibers help in grasping the ground.
Backbone: Backbone or vertebral section is made out of 33 little ring like bones called vertebrae. It is an empty hard cylinder.
Ball and socket joint:A joint where adjusted finish of one bone fits into the depression of different bones.
Bristles: Hair like structures anticipating out of the assemblage of night crawlers. With the assistance of these, it fixes itself with the ground.
Cartilage: It is the extra piece of the skeleton that isn’t as hard as the bones and which can be twisted moreover.
Cavity:The bowl like part (empty space) in the shoulder bone permits the adjusted finish of the arm issue that remains to be worked out into it to frame ball and attachment joint.
Fixed joints: Some of the joints permit no development. These are called fixed joints. For example joints in the skull and upper jaw.
Gait of animals: Some creatures don’t have bones. They have muscles which help to broaden and abbreviate the body. During development, creature initially broadens the forward portion of the body, keeping the back position fixed to the ground. After that creature fixes the front end and discharges the backside. Presently creature abbreviates the body and pulls the backside forward. During this training creature pushes ahead by a little separation.
Hinge joint: Hinge joint is found in the fingers, elbow and knee. It permits development just one way.
Muscle: Muscles are engaged with the development of bones.
External Skeleton: Skeleton discovered outside the body is called external skeleton, e.g., hair and nails in human.
Pelvic bones: Bones in the hip district are called pelvic bones.
Pivotal joint:The joint where our neck joins the head is a vital joint.
Rib cage: Ribs join the chest bone and the spine together to shape a container. This is called rib confinement.
Shoulder bones: The shoulder bones are the two bones of the shoulders.
Skeleton: The structure of the body which is comprised of bones and ligament is called a skeleton.
Streamlined: The body shape where body tightens at the two finishes is called smoothed out body, e.g., collection of fowls and fish.
(Chapter 8: Body movements)

