The s-Block Elements: Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Chapter 10

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 10 – The s-Block Elements
In the last chapter 9, you learned about Hydrogen in detail. In this chapter: The s-block elements, you will learn about that out of the considerable number of elements in the intermittent table, the s block elements are the most known and utilized. Elements like calcium, sodium, and potassium are mostly individuals belonging to the s block. They are precious elements. The various aspects in the s block have remarkable properties and use. We should find out about these elements and the s block of the periodic table in detail.
Each item around us shows some unique qualities, which puts aside that object from the rest. These properties become the motivation behind why a component acts in a specific way and how we can foresee its conduct. We will find out about the attributes of the compounds of the soluble base earth metals in this theme. How are the compounds of the soluble base earth metals and not the same as the compounds of different elements in the periodic table? How about we discover.
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
Quick Revision notes:
General Electronic Configuration of s-Block ElementsFor soluble base metals [noble gas] ns1 For alkaline earth metals [noble gas] ns2
-
Group 1 Elements: Alkali metals
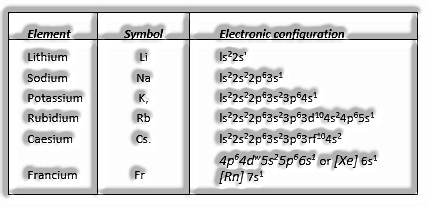
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
Electronic Configuration, ns1, where n speaks to the valence shell.
These elements are called antacid metals since they promptly break up in water to frame dissolvable hydroxides, which are absolutely alkaline in nature.
-
Ionization Enthalpy
The ionization enthalpies of the soluble base metals are commonly low and lessening down the group from Li to Cs.
Reason: Since antacid metals have huge atomic sizes because valence s-electron (ns1) can be quickly evacuated. These qualities decline down the group due to diminishing in the greatness of the power of fascination with the core because of expanded atomic radii and screening impact.
-
Hydration Enthalpy
Littler, the size of the particle, more is its inclination to get hydrated. Henceforth more is the hydration enthalpy. Hydration enthalpies of salt metal ions decline with increment in ionic sizes.
Li+ > Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+
-
Physical Properties
(I) All the salt metals are shiny white, soft, and light metals.
(ii) They commonly have a low thickness, which increments down the group.
(iii) They give shading to an oxidizing fire. This is because the warmth from the fire energizes the furthest orbital electron to a higher vitality level. When the energized electron returns to the ground state, there is an outflow of radiation in the noticeable area.
-
Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals
(I) Reaction with air:

At the point when presented to the air surface of the antacid metals, get discolored due to the development of oxides and hydroxides.
Salt metals consolidate with oxygen after warming to shape various oxides relying on their tendency.
(ii) Reaction with water:
Alkali metals on reaction with water form hydroxide and hydrogen
(iii) Reaction with hydrogen:
The alkali metals get combined with hydrogen at about 673 K (lithium at 1073 K) to form hydrides.
2M + H2 ————-> 2M+
The ionic character of hydrides increases from Li to Cs.
(iv) Reaction with halogens:
A direct combination of alkali metals with halogens gives metal halides.
2M + X2————–> 2MX
They have comparatively high melting and boiling points.
Order of reactivity of M:
![]()
Employments of Sodium
(I) Used as sodium amalgam in a research facility (a combination of organic compounds).
(ii) Sodium is utilized in sodium fume light.
(iii) In the liquid state, it is utilized in atomic reactors.
(iv) A compound of sodium-potassium is utilized in high-temperature thermometers.
Employments of Potassium
(I) Salts of potassium are utilized in manures.
(ii) Used as a diminishing operator.
Employments of Cesium
(I) In rocket propellent
(ii) In photographic cells.
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
-
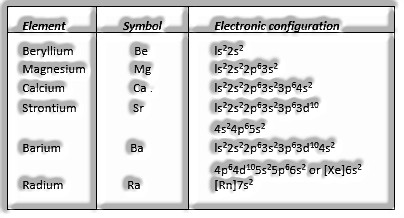
Group 2 Elements: Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkaline Earth Metals: It was a name given to them as they are alkaline exactly like soluble base metals oxides, and they were found in the world’s outside layer.
Model, Be (Beryllium), Ca, Mg, Sr, and so forth.
- Electronic Configuration Their overall electronic configuration is spoken to as [noble gas] ns2.
(v) Reducing nature:
The soluble base metals are dependable decreasing specialists. In the watery arrangement, it has been seen that the decreasing character of soluble base metals follows the grouping Na < K < Rb < Cs < Li, Li is the most grounded while sodium is a least ground-breaking lessening specialist. This can be clarified as far as cathode possibilities (E°). Since the anode capability of Li is the most reduced. Therefore Li is the most grounded decreasing specialist.
(vi) Solubility in liquid ammonia:
The antacid metals disintegrate in liquid ammonia to give the dark blue arrangement. The arrangement is directed in nature.
M+ (x + y) NH3 — – > [M (NH3) X]+ + [e (NH3) y]–
The moment light falls on the ammoniated electrons, they retain vitality relating to red shading, and the light which radiates from it has blue shading. In the concentrated arrangement, shading changes to bronze. The blue solutions are paramagnetic, and the concentrated solutions are diamagnetic.
-
Uses of Alkali Metals
Employments of Lithium
(I) Lithium is utilized as a deoxidizer in the filtration of copper and nickel.
(ii) Lithium is used to make both primary and secondary batteries.
(iii) Lithium hydride is utilized as a wellspring of hydrogen for meteorological purposes.
(iv) Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) is a decent decreasing specialist.
(v) Lithium carbonate is utilized in making glass.
Employments of Sodium
(I) Used as sodium amalgam in a research facility (a combination of organic compounds).
(ii) Sodium is utilized in sodium fume light.
(iii) In the liquid state, it is being used in atomic reactors.
(iv) A compound of sodium-potassium is utilized in high-temperature thermometers.
Employments of Potassium
(I) Salts of potassium are utilized in manures.
(ii) Used as a diminishing operator.
Employments of Cesium
(I) In rocket propellent
(ii) In photographic cells.
-
Group 2 Elements: Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkaline Earth Metals: They were specified alkaline earth metals since they were alkaline like soluble base metals oxides, and they were found in the world’s outside layer.
Model, Be (Beryllium), Ca, Mg, Sr, and so forth.
- Electronic Configuration Their overall electronic Configuration is spoken to as [noble gas] ns2.
-
Atomic and Ionic Radii
Both the Atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals one nearly littler than alkali metals. Inside the group, atomic and ionic radii increments with the expansion in the atomic number. Reason: Because these elements have just two valence electrons and the greatness of the power of fascination with the core is very little.
-
Ionization Enthalpies
These metals likewise have low ionization enthalpies because of the genuinely enormous size of atoms. As the atomic dimensions increment down, the group ionization enthalpies are relied upon to diminish similarly. Because of their small size compared with alkali metals, first ionization enthalpies of alkaline earth metals are higher than those of alkali metals.
-
Hydration Enthalpies
The hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions are more significant than those of the alkali metals. Along these lines, alkaline earth metals tend to become hydrated. The hydration enthalpies diminish down the group since the cationic size increments.
Be2+ > Mg2+ > Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+
Metallic character: They have stable metallic bonds when contrasted with the alkali metals in a similar period. This is because of the latter part size of alkaline earth metal and two valence electrons present in the outer shell.
-
Physical Properties
(I) They are more enthusiastic than alkali metals.
(ii) M.P. and B.P. are higher than the relating alkali metals because of their tiny size.
(iii) The electropositive character increments down the group.
(iv) Except for Be and Mg, every one of these metals bestow trademark shading to the fire.
(v) The alkaline earth metals have high warm and electrical conductivity.
-
Chemical Properties
- Reaction with oxygen. Beryllium and magnesium are dynamically idle to oxygen due to the development of a thin film of oxide on their surface.
Reactivity towards oxygen increments as going down the group.
- Reaction with water. For a fact, alkali metals are more electropositive than these metals and hence they are less receptive to water.
Magnesium responds with bubbling water or steam. The rest of the individuals react even with cold water.
Mg + 2H20 — – > Mg(OH)2 + H2
Ca + 2H20 — > Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Reaction with incandescent light. They join with the incandescent lamp at a suitable temperature to frame comparing halides MX2.
M + X2 — – > MX2 (X = F, Cl, Br, I)
Warm decay of (NH4)2 BeF4is was utilized for the readiness of BeF2.
- Reaction with hydrogen. These metals aside from Be consolidate with hydrogen legitimately after warming to shape metal hydrides
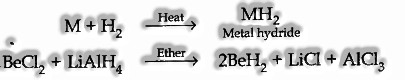
- General Feature of Compounds of Alkaline Earth Metals
Oxides and Hydroxides
(I) To frame MO, The alkaline earth metals burn in oxygen. (monoxide).
(ii) These oxides are entirely steady to warm.
(iii) BeO is amphoteric in nature, while oxides of different elements are ionic.
(iv) Except for BeO, they are essential in nature and respond with water to frame sparingly dissolvable hydroxides.
MO + H2O — – > M(OH)2
(v) Hydroxides of alkaline earth metals are less steady and less essential than alkali metal hydroxides.
(vi) Beryllium hydroxide is amphoteric in nature.
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
Halides
The alkaline earth metals consolidate legitimately with incandescent light at suitable temperatures shaping halides, MX2.
They can likewise be set up by the activity of halogen acids (H.X.) on metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides.
M + 2HX — – > MX2 + H2
MO + 2HX — > MX2 + H20
M (OH)2 + 2HX — – > MX2 + 2H20
(I) Except for beryllium halides, every single other halide of alkaline earth metals is ionic in nature.
(ii) Except BeCl2 and MgCl2 other chlorides of alkaline earth metals confer trademark hues to fire.
![]()
(iii) down the group, the tendency to form hydrides decreases.
For example, (MgCl2– 8 H20, CaCl2– 6 H20, SrCl2– 6 H20, BaCl2– 2 H2O)
(iv) BeCl2 has a chain structure in the solid phase, as shown below.
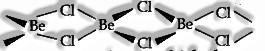
In the fume stage, the compound exists as a dimer, decaying at about 1000K to give a monomer in which the Be atom is in sp hybridization state.
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
Sulphates
(I) The sulphates of alkaline earth metals came out to be white solids and very steady to warm.
(ii) BeS04 and MgS04 are promptly dissolvable in water. Solubility diminishes from BeS04 to BaS04.
Reason. Because of more prominent hydration enthalpies of Be2+ ions and Mg2+ ions, they conquer the cross-section enthalpy factor. Their sulfates are solvent in water.
Carbonates
Carbonates of alkaline earth metals are thermally precarious and break down on warming.

- Some Important Compounds of Calcium

Uses:
(i) In the manufacture of cement, sodium carbonate, calcium carbide, etc.
(ii) Used in the purification of sugar.
(iii) In the manufacture of dyestuffs.

Employments:
(I) It is utilized in the assembling of building material.
(ii) Used in white-wash as a disinfectant.
(iii) Used to identify C02 gas in the research center.
(iii) Calcium Carbonate or Limestone (CaC03)
Planning: Calcium carbonate happens in nature in various structures like limestone, marble, chalk, and so forth. It tends to be set up by going C02 through slaked lime in a constrained sum.
Ca(OH)2 + C02 — > CaC03 + H20
It can likewise be arranged by the reaction of an answer of sodium carbonate with calcium chloride.
CaCl2 + Na2C03 — > CaC03 + 2NaCl

Uses:
(I) In the assembling of Quick Lime.
(ii) MgC03 is utilized as a motion in the extraction of metals.
(iii) Used as an antacid.
(iv) In the production of top-notch paper.
(iv) Calcium Sulphate (Plaster of Paris) CaS04-1/2H20
Readiness: It is gotten when gypsum CaS04–2 H20 is warmed to 393 K
2(CaS04-2H20) — – > 2(CaS04) . H20 + 3H20
Over 393 K anhydrous CaS04 is framed, which is called ‘dead consumed mortar.’
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)
Properties:
(I) It is a white amorphous powder.
(ii) When it is an insufficient blended amount of water, it frames a hard plastic mass inside 15 minutes.
Employments:
(I) Commonly utilized in making stoneware, pottery, and so forth.
(ii) Used in the careful bandages for setting the broken bone or sprain.
(iii) For making sculptures, elaborate work, brightening material, and so forth.
(v) Cement
Arrangement: Prepared by joining a material rich in CaO with other materials, such as earth, which contains Si02 alongside the oxides of aluminum, iron, and magnesium.
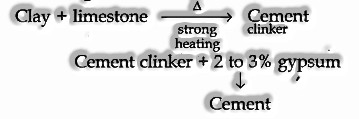
Essential Ingredients of portland cement:
(Ca2Si04) dicalcium silicate 26%
(Ca2SiO4) Tricalcium silicate 51%
(Ca3Al206) Tricalcium Aluminate 11%
Uses:
In plastering and in construction purposes.
- s-block elements constitute Group I and II elements.
- General electronic configuration of
Group I = [Noble gas] ns1
Group II = [Noble gas] ns2
- Diagonal Relationship
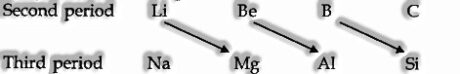
The initial three elements of the second period (Li, Be, B) show corner to corner comparability with the elements (Mg, Al, Si) of the third period. Such similitudes are named as a corner to corner relationship.
- The alkali metals are gleaming white soft metals. They are profoundly receptive. Their watery solutions are firmly alkaline in nature. Their atomic and ionic sizes increase in descending the group, and ionization enthalpies decline methodically.
- Alkaline earth metals. They are a lot like alkali metals; however, because of little size, a few contrasts are there. Their oxides and hydroxides are less fundamental than the alkali metals.
The electrolysis of aq NaCl sets up • Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in the Castner-Kellner cell.
Slaked lime Ca(OH)2 is framed by the activity of fast lime on water.
- Gypsum is CaS04. 2 H20. On warming up to 390 K CaS04/2H20 (mortar of Paris) is framed.
Hence, moving down the group, the solubility of sulphates of alkaline earth metal decreases primarily due to reduction in hydration enthalpy which was Be2+ and became Ba2+ later. High solubility of Be2+ and Mg2+ ions due to the smaller size accounts for high solubility of BeSO4 and MgSO4. The reason being the sulphates of alkaline earth metals decompose on heating giving their corresponding oxides and SO3.
(The s-Block Elements: Class 11)

