Surface Areas And Volumes: Class 10 Mathematics NCERT Chapter 13

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 13 – Surface Areas and Volumes
In the last chapter 12, you learned about Areas Related to Circles. In this chapter, Surface Areas and Volumes, you will learn everything about it.
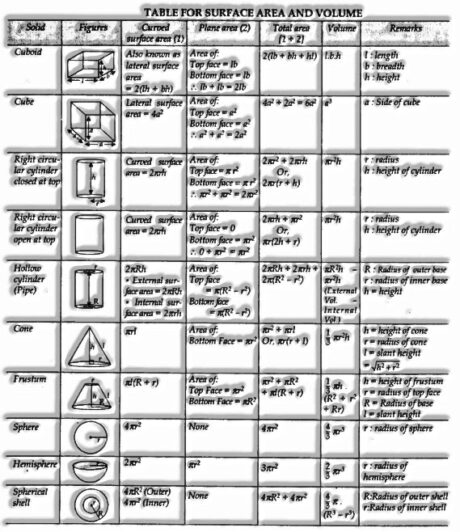
Cuboid and its Surface Area
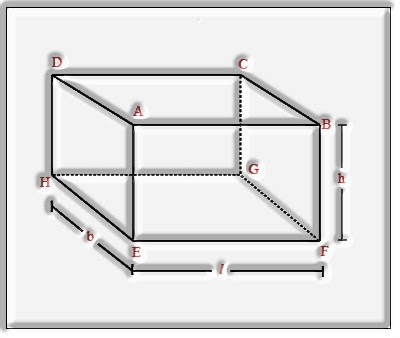
The surface area of a cuboid is equivalent to the total of the areas of its six rectangular faces. Consider a cuboid whose measurements are l × b × h individually.
Cuboid that has length l, breadth b and height h
The absolute surface area of the cuboid (TSA) = Sum of the areas of all its six faces
TSA (cuboid) = 2(l × b) + 2(b × h) + 2(l × h) = 2(lb + bh + lh)
Horizontal surface area (LSA) is the area of the apparent multitude of sides separated from the top and base faces.
The parallel surface area of the cuboid = Area of face AEHD + Area of face BFGC + Area of face ABFE + Area of face DHGC
LSA (cuboid) = 2(b × h) + 2(l × h) = 2h(l + b)
Length of side of a cuboid =√(l2 + b2 + h2)
Right Circular Cone and its Surface Area
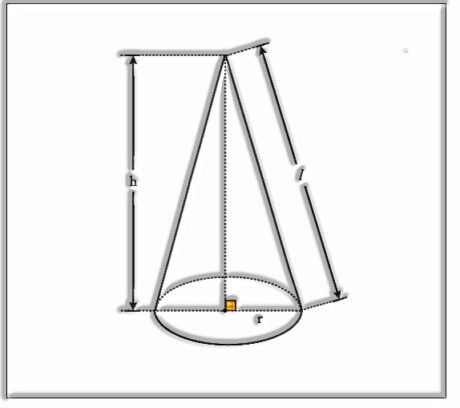
Think about a right angular cone with incline length l, radius r and height h.
Cone with the base radius r and height h
CSA of right round cone = πrl
TSA is equal to CSA + area of base = πrl + πr2 = πr(l + r)
Sphere and its Surface Area
For a sphere of radius r
Curved Surface Area (CSA) = complete Surface Area (TSA) = 4πr2
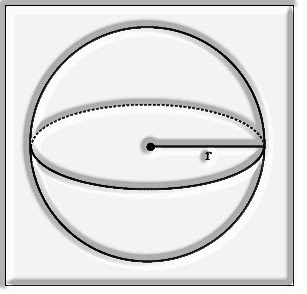
Sphere with radius r
SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME OF COMBINATIONS
Cone over a Cylinder.
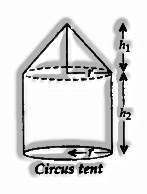
r = radius of cylinder and cone;
h1 = height of the cone
h2 = height of cylinder
All out Surface area is equal to Curved surface area of cone + Curved surface area of cylinder + area of round base
= πrl + 2πrh2 +πr2;
Inclination height,
Total Volume is equal to Volume of cone + Volume of cylinder
Cone over a Hemisphere:
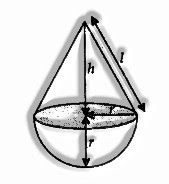
h = height of cone;
l = incline height of cone =
r = radius of cone and hemisphere
Total Surface area is equal to Curved surface area of cone + Curved surface area of hemisphere = πrl + 2πr2
Volume is equal to Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere =
Funnel shaped Cavity in Cylinder
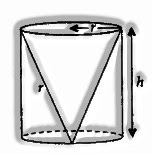
r = radius of cone and cylinder;
h = height of cylinder and funnel shaped cavity;
l = Slant height
Total Surface area is equal to Curved surface area of cylinder + Area of base face of cylinder + Curved surface area of cone = 2πrh + πr2 + πrl
Volume is equal to Volume of cylinder – Volume of cone
Cones on Either Side of Cylinder.
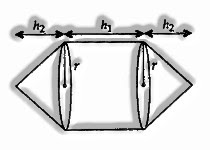
r = radius of cylinder and cone;
h1 represents height of cylinder
h2 represents height of cones
Inclination height of cone,
Surface area is equal to Curved surface area of 2 cones + Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrl + 2πrh1
Volume = 2(Volume of cone) + Volume of cylinder
Cylinder with Hemispherical Ends.
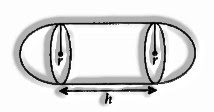
r = radius of cylinder and hemispherical closures;
h = height of cylinder
Total surface area is equal to Curved surface area of cylinder + Curved surface area of 2 hemispheres = 2πrh + 4πr2
Volume is equal to Volume of cylinder + Volume of 2 hemispheres
Hemisphere on Cube or Hemispherical Cavity on a Cube
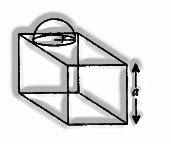
a = side of cube;
r = radius of hemisphere.
Surface area is equal to Surface area of a cube– Area of hemisphere face + Curved surface area of hemisphere
= 6a2 – πr2 + 2πr2 = 6a2 + πr2
Volume = Volume of a cube + Volume of hemisphere
Hemispherical Cavity in Cylinder
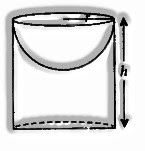
r = radius of hemisphere;
h = height of cylinder
Complete surface area = Curved surface area of cylinder + Surface area of base + Curved surface area of hemisphere
= 2πrh + πr2 + 2πr2 = 2πrh + 3πr2
Total Volume is equal to Volume of cylinder – Volume of hemisphere =

