Nutrition in Plants: Class 7 Science NCERT Chapter 1

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants
In this year, we will learn about basics of our environment science related. In this chapter, Nutrition in Plants, we will learn how plants get their nutrition.
Quick revision notes
All living beings require food. The food offers vitality to the life forms for development and support of their body capacities. Sugars, proteins, fats, nutrients and minerals are the parts of food. These parts of food are fundamental for our body and are called supplements.
Nourishment is the way toward taking food by a living being and its use by the body. Green plants set up their own food while people and creatures are legitimately or by implication subject to plants for their food.
Methods of Nutrition
Based on an alternate method of nourishment, living beings are classified into two significant sorts, for example
(I) Autotrophs (auto-self, trobpos-sustenance) Autotrophic nourishment is the method of sustenance where creatures make their own food from the straightforward substance (for example CO2 and H2O) by the cycle of photosynthesis. In this manner, plants are called autotrophs.
(ii) Heterotrophs (heteros-other) Humans and creatures don’t contain chlorophyll and are reliant on plants for their food in readymade structure. Those life forms which can’t set up their own food and take food from green plants or creatures are called heterotrophs and the method of sustenance is called heterotrophic nourishment.
Photosynthesis: Food Making Process in Plants
The cycle by which autotrophic green plants make their own food from straightforward inorganic substances (carbon dioxide and water) within the sight of daylight and green shade or chlorophyll is known as photosynthesis.
Site of Photosynthesis
The cycle of photosynthesis happens in green leaves, accordingly leaves are alluded to as the food industrial facilities of plants. The. the photosynthetic cycle can happen in other green pieces of the plant-like stem yet isn’t sufficient for addressing all the requirements of the plant.
Responses Involved in Photosynthesis
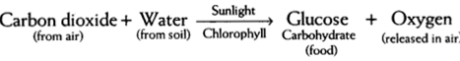
The entire cycle of photosynthesis can be given by the accompanying condition:
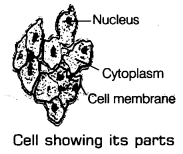
Cells
All living beings are produced using little structure units of catted cells. Cells are the auxiliary and practical units of the body of every living life form. They must be seen under a magnifying instrument. The phone has a slim external limit called cell film, an unmistakable, midway found round structure called core and jam the substance encompassing the core called cytoplasm.
The inorganic crude material, for example CO2 is taken from the air through the small pores present on the outside of leaves called stomata and water is assimilated through the underlying foundations of plants (from the dirt) and is shipped to leaves by vessels which act like funnels. These vessels structure the persistent way from roots to leaves for the development of supplements.
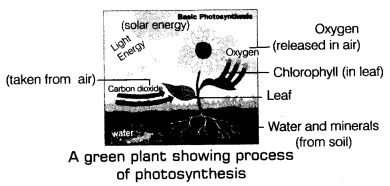
Green plants have chlorophyll in their leaves which catches the vitality of the daylight. This light vitality is utilized to get ready food (starch). During the cycle, oxygen is additionally delivered. Photosynthesis is the remarkable cycle in which sun oriented vitality is caught by the leaves and put away in the plants as food. Hence, ‘Sun is a definitive wellspring of vitality for all the living beings.’
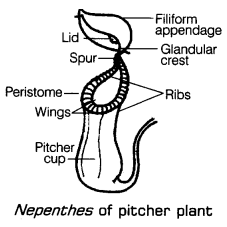
Insectivorous Plants
There are a few plants which can trap bugs and summary them for their nourishment. These plants are green in shading yet need nitrogen components. To conquer this issue, these plants eat creepy crawlies. Henceforth they are called insectivorous plant or rapacious plants. These have particular leaves, the zenith of which frames a top that can open and close the mouth of pitcher. There are hair inside the pitcher which are utilized to snare the creepy crawlies.
At the point when a creepy crawly comes in contact of the cover, it gets shut and traps the bugs. The bug inside the pitcher is processed by stomach related juices discharged by the pitcher to acquire nitrogen mixes (amino acids) from them.
for example pitcher plant, sundew, Venus flytrap and bladderwort.
Since these can incorporate their own food however satisfy their nitrogen inadequacy by eating bugs, in this manner these are called as fractional heterotrophs.
Saprotrophic Plants
The mode of nutrition in which organisms take their nutrients from dead and decaying matter is called saprotrophic nutrition.
Plants which use the saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called saprotrophs, e.g. fungi like mushrooms are non-green plants that grow on the dead and decaying matter for their food. Bread moulds (fungi) and yeast are saprophytic plants.
Saprotrophic Plants
The method of nourishment wherein life forms take their supplements from dead and rotting matter is called saprotrophic sustenance.
Plants which utilize the saprotrophic method of sustenance are called saprotrophs, for example growths like mushrooms are non-green plants that develop on the dead and rotting matter for their food. Bread molds (organisms) and yeast are saprophytic plants.
Cooperative Plants
Some of the time, two plants of various species live respectively and help each other in acquiring food and asylum. This affiliation is called advantageous interaction and such plants are called cooperative plants.
The relationship where two unique living beings live respectively and offer haven and supplements is called harmonious relationship, for example lichens and Rhizobium.
Lichen is a relationship where green growth and an organism live respectively. The parasite gives sanctuary, water and minerals to the green growth and consequently, the green growth give food which it plans by photosynthesis.
Recharging of Nutrients in Soil
Harvests require a ton of nitrogen to make proteins. After the collect, the dirt gets lacking in nitrogen. Plants can’t utilize the nitrogen gas accessible in the climate legitimately. The activity of specific microorganisms can change over this nitrogen into a structure promptly utilized by plants. Rhizobium microbes live in the root knobs of leguminous plants. These microorganisms take nitrogen gas from the air and convert it into water-solvent nitrogen mixes making it accessible to the leguminous plants for their development.
Consequently, leguminous plants give food and haven to the microbes as Rhizobium can’t set up its food. They, accordingly have an advantageous relationship. This affiliation is significant for the ranchers, as they don’t have to add nitrogen manures to the dirt in which leguminous plants are developed.

