Metals and Non-metals: Class 10 Science NCERT Chapter 3
- Home
- Class 10 science
- Metals and Non-metals: Class 10 Science NCERT Chapter 3

Characteristics of NCERT Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals
In the last chapter 2, you all learned about Acid, Bases and Salts. In this chapter, you all will learn about Metals and Non-metals.
Quick Revision Notes
Metals: Physical properties of metals, compound properties of metals, and non-metal oxide.
Metals are the elements that direct warmth and electricity and are moldable and bendable. Models are Iron (Fe), Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Platinum (Pt), Lead (Pb), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) and so on.
Metals are elements that structure positive particles by losing electrons. Subsequently, metals are known as Electropositive Elements.
Physical Properties of Metals
- Hardness: Most metals are hard, apart from alkali metals, such as sodium, and so on are delicate metals. These can be cut into pieces using blades.
- Quality: Most of the metals are solid and have high rigidity. Along these lines, large structures are made utilizing metals, for example, copper (Cu) and iron (Fe). (But Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) which are delicate metals).
- State: Metals are solid at room temperature, aside from mercury (Hg).
- Sound: Metals produce a ringing sound. In this way, metals are called Sonorous. The metals’ sound is called Metallic sound. That’s why metal wires are utilized in making instruments.
- Conduction: Metals are a decent transmitter of warmth and electricity. That’s why electric wires are made up of metals like copper and aluminum.
- Malleability: Metals are pliable and hence can be beaten into a meager sheet. As a result of this property, iron is utilized in making huge boats.
- Ductility: Metals are flexible. This implies metals can be brought into a dainty wire. In view of this property, a wire is made of metals.
- Melting and Boiling Point: Metals commonly have high melting and boiling points. (But sodium and potassium metals which have low melting and boiling point.)
- Thickness: Most of the metals have a high thickness.
- Shading: Most of the metals are dim in shading. However, gold and copper are special cases.
Chemical Properties of Metals
- Reaction with oxygen: Most of the metals structure individual metal oxides while responding with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Models:
The Reaction of Potassium with Oxygen: Potassium metal structures potassium oxide when the response with oxygen.
The Reaction of Sodium with Oxygen: Sodium metal structures sodium oxide when the response with oxygen.
Lithium, potassium, sodium, and so forth are known as Alkali-metals. Alkali metals respond vivaciously with oxygen.
The Reaction of Copper metal with Oxygen: Copper doesn’t respond with oxygen at room temperature, yet when consumed in air, it gives oxide.
Silver, gold, and platinum don’t join with the oxygen of air even at high temperatures. They are the least reactive.
- The Reaction of metals with water: Metals structure separate hydroxide and hydrogen gas while responding with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
The greater part of the metals doesn’t respond with water. In any case, alkali metals respond enthusiastically with water.
The Reaction of Na metal with Water: Sodium metal structures sodium hydroxide and frees hydrogen gas alongside part of warmth while responding with water.
The Reaction of Calcium metal with Water: Calcium structures calcium hydroxide alongside hydrogen gas and warmth when responding with water.
The Reaction of Magnesium metal with Water: Magnesium metal responds with water gradually and structures magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
.
At the point when steam is ignored, magnesium metal, magnesium oxide, and hydrogen gas are framed.
The Reaction of Aluminum metal with Water: The Reaction of aluminum metal with cold water is too delayed to even consider coming into notice. In any case, when steam is ignored, aluminum metal, aluminum oxide, and hydrogen gas are delivered.
2Al + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 2H2
The Reaction of Zinc metal with Water: Zinc metal produces zinc oxide and hydrogen gas when steam is disregarded. Zinc doesn’t respond with cold water.
The Reaction of Iron with Water:The Reaction of iron with cold water is exceptionally moderate and comes into notice after quite a while. Iron structures rust (iron oxide) when responds with dampness present in the air. Iron oxide and hydrogen gas are framed by ignoring steam iron metal.
Both (Ca) and magnesium(Mg) are heavier than water yet glide over it: Both calcium and magnesium coast over the water surface since hydrogen gas is advanced when these metals respond with water. It is like air pockets that stick on the metal surface. Accordingly, they glide over it.
Different metals normally don’t respond with water or respond gradually. Lead, copper, silver, and gold don’t respond with steam. In this way, the request for reactivity of different metals towards water might be composed as given underneath:
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Ae > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag > Au
- The Reaction of metals with dilute acid: Metals structure individual salts while responding with dilute acid.
Metal + dil. acid → Metal salt + Hydrogen
The Reaction of Sodium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Sodium metal gives sodium chloride and hydrogen gas when responding with dilute hydrochloric acid.
.
Reaction of Magnesium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas are shaped when magnesium responds with dilute hydrochloric acid.
The Reaction of Zn with dilute sulphuric acid:Zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are shaped when Zinc responds with dilute sulphuric acid. This technique is utilized in the research facility to deliver hydrogen gas.
Hydrogen (H2) gas isn’t developed when metal is treated with nitric acid (HNO3):
Nitric acid is a solid oxidizing operator, and it oxidizes the hydrogen gas (H2) freed into water (H2O), and itself gets diminished to some nitrogen oxides like nitrous oxide (N2O)3, etc.
Copper, silver, gold are known as noble metals. These don’t respond with water or dilute acids.
The request for reactivity of metal towards dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid is in the right;
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Hg > Ag
Oxides of metals
Substance Properties: Metal oxides have a basic nature. Metal Oxides’s aqueous solution turns red litmus blue.
The Reaction of Metal oxides with Water: Most of the metal oxides are insoluble in water. Alkali metal oxides are soluble in water. Alkali metal oxides give a solid base when dissolved in water.
The Reaction of Sodium oxide with Water: Sodium oxide gives sodium hydroxide when the response with water.
The Reaction of Potassium oxide with Water:Potassium oxide gives potassium hydroxide when the response with water.
The Reaction of Zinc oxide and Aluminium oxide:vAluminum oxide and zinc oxide are insoluble in water. Zinc oxide and aluminum oxides are amphoteric. An amphoteric substance has both basicity and acidity. It responds with a base like acid and reacts with an acid like a base.
At the point when zinc oxide responds with sodium hydroxide, it carries on like acid. In this particular Reaction, sodium zincate and water are shaped.
Zinc oxide acts like a base when it responds with acid. Zinc oxide produces Zinc chloride and water on Reaction with hydrochloric acid.
Along these lines, aluminum oxide carries on like a base when responding with acid and acts like acid when responding with the base.
Aluminum oxide gives sodium aluminate alongside water when the response with sodium hydroxide.
Aluminum oxide gives aluminum chloride alongside water when it responds with hydrochloric acid.
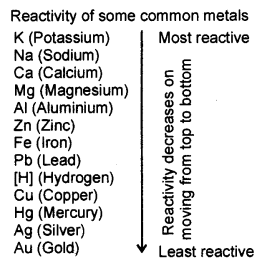
The Reactivity Series of Metals: The request for force or reactivity of metal is known as Reactivity Series. Reactivity of elements diminishes on moving through and through in the given reactivity arrangement.
In the reactivity arrangement, copper, gold, and silver are at the base and, thus, least reactive. These metals are known as Noble metals. Potassium is at the head of the arrangement and, consequently, generally reactive.
Reactivity of certain metals are provided in descending request :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
- The Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts: Reaction of metals with other metal salt solution is a displacement reaction. In this Reaction, less reactive metal is displaced by the more reactive metal.
Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Models :
Iron displaces copper from copper sulfate solution.
Essentially, aluminum and Zinc displace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
In all the above models, iron, aluminum, and Zinc are more reactive than copper. This is the reason they displace copper from its salt solution.
At the point when copper is dipped in the solution of silver nitrate, it displaces silver and structures copper nitrate.
In the Reaction, copper is more reactive than silver and subsequently displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
Silver metal doesn’t respond with a copper sulfate solution since silver is less reactive than copper and not ready to displace copper from its salt solution.
Likewise, when gold is dipped in the solution of copper nitrate, no reaction happens in light of the fact that copper is more reactive than gold.
Comparatively, no reaction happens when copper is dipped in an aluminum nitrate solution since copper is less reactive than aluminum.
Non-Metals: Physical Properties of nonmetals, substance properties of nonmetals, non¬metal oxides, Reaction of metal and Non-metal, Ionic bonds, and anionic arrangement bonds. Non-metals are the elements that don’t direct electricity and are neither malleable nor bendable.
Models: Carbon (C), Sulfur (S), Phosphorous (P), Silicon (Si), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Neon (Ne) and Argon (Ar) and so forth.
Non-metals are the elements that structure negative particles by increasing an electron. Subsequently, non¬metals are otherwise called Electronegative Elements.
Physical properties of nonmetals
- Hardness: Non-metals are not hard; rather, they are commonly delicate. However, the diamond is a special case; it is the hardest normally occurring substance.
- State: Non-metals might be solid, liquid, or gas.
- Shine: Non-metals have a dull appearance. Diamond and iodine are exceptional cases.
- Vibrancy: Non-metals are not resonant, i.e., they don’t create a familiar sound on being hit.
- Conduction: Non-metals are a terrible conduit of warmth and electricity. Graphite, an allotrope of carbon, is a decent electricity channel and is an exemption.
- Malleability and ductility: Non-metals are fragile.
- Melting and boiling point: Non-metals commonly have low melting and boiling points.
- Thickness: Most of the non-metals have low thickness.
- Shading: Non-metals are in numerous hues.
- Carbon as graphite is non-metal, which leads to electricity.
- Iodine is non-metal, which is glistening, having a sparkling surface.
- Carbon as diamond is a non-metal, which is very hard.
- Diamond is a non-metal which has a high melting point and boiling point.
Substance properties of Nonmetals
- The reaction of Non-metals with Oxygen: Non-metals particular structure oxide while responding with oxygen.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metallic oxide
At the point when carbon responds with oxygen, carbon dioxide is shaped alongside the production of warmth.
At the point when carbon is sung in a deficient flexibly of air, it structures carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is a harmful substance. Breathing in of carbon monoxide may demonstrate lethal.
Sulphur gives sulfur dioxide while responding with oxygen. Sulphur bursts into flames when presented to air.
At the point when hydrogen responds with O2, it gives water.
Non-metallic Oxide: They are acidic in nature. The solution of non-metal oxides changes the litmus paper red.
CO2 gives carbonic acid when dissolved in H2O.
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphurous acid when dissolved in water.
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphuric acid when responding with oxygen.
- The Reaction of Non-metal with Chlorine: Non-metal gives individual chloride when they respond with Cl.
Non-metal + Chlorine → Non-metal chloride
Hydrogen gives HCl, and phosphorous gives phosphorous trichloride while responding with chlorine.
- Reaction of Non-metals with Hydrogen: Non-metals reactive with hydrogen to shape covalent hydrides.
Non-metal + Hydrogen → Covalent Hydride
Sulphur joins with hydrogen to frame a covalent hydride is called Hydrogen sulphide.
Nitrogen consolidates with hydrogen in the nearness of an iron impetus to shape covalent hydride smelling salts.
Non-metals don’t respond with water (or steam) to advance Hydrogen gas.
Non-metals don’t respond with dilute acids.
- The reaction of Metal and Non-metal: Many metals structure ionic bonds when they respond with non-metals. Compounds so framed are known as Ionic Compounds.
Particles: Positive or negative charged atoms are known as particles. Particles are framed as a result of misfortune or the addition of electrons. Atoms structure particles get by the electronic design of the closest noble gas.
Positive particle: A positive particle is framed in view of the loss of electrons by an atom.
The following are a few instances of positive particles:
Sodium structures sodium particles on account of the loss of one electron. As a result, one certain charge comes over sodium.
Magnesium structures positive particles due to the loss of two electrons. Two positive charges come over magnesium due to the loss of two electrons.
Negative ion:A negative particle is shaped due to the addition of an electron.
A few models are given underneath :
Chlorine increases one electron so as to accomplish a steady design. After the loss of one electron, Cl acquires one negative charge over it, shaping chlorine particle.
Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are framed based on the transfer of electrons from the metal to non¬metal. In this course, metals get a positive charge due to the transfer of electrons, and nonmetal gets a negative charge as a result of the acknowledgment of electrons. As it were, bond shaped among positive and negative particles is called Ionic Bond.
Since a compound is electrically unbiased, the two particles must be consolidated to frame an ionic compound, negative and positive.
A few models are given underneath:
Development of Sodium Chloride (NaCl): In sodium chloride, sodium is a metal (alkali metal), and chlorine is a non-metal.
The atomic number of sodium = 11
Electronic design of sodium: 2, 8, 1
Number of electrons in furthest circle = 1
Valence electrons = Electrons in peripheral circle = 1
The atomic number of chlorine = 17
Electronic setup of chlorine: 2, 8, 7
Electrons in peripheral circle = 7
Hence, valence electrons =?
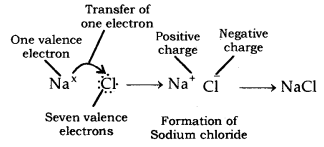
Na has one valence electron, while Cl has seven valence electrons. Sodium requires losing one electron to acquire a stable setup, and chlorine requires increasing one electron so as to get a steady electronic arrangement. Subsequently, so as to acquire a stable setup, sodium transfers one electron to chlorine, and sodium gets one positive charge (+), and chlorine gets one negative charge after the addition of one electron. Sodium chloride is framed in view of the transfer of electrons.
Consequently, the ionic bond is shaped among sodium and chlorine. Since sodium chloride is framed due to ionic bond, hence, it is called an Ionic compound. Incomparable manner, potassium chloride (KCl) is shaped.
Properties of Ionic compound
- Ionic compounds are solid. Ionic bond has a more prominent power of fascination in view of which particles draw in one another firmly. This makes ionic compounds solid.
- Ionic compounds are weak.
- Ionic compounds have high boiling and melting points since the power of fascination between particles of ionic compounds are solid.
- Ionic compounds, by and large, dissolve in water.
- Ionic compounds are commonly insoluble in organic solvents, like lamp oil, petroleum, and so forth.
- Ionic compounds don’t direct electricity in the solid-state.
- The solution of ionic compounds is indirect water electricity. This is because the presence of the particles in the solution of ionic compounds encourage the section of electricity by moving towards inverse cathodes.
- Ionic compounds lead electricity in the liquid state.
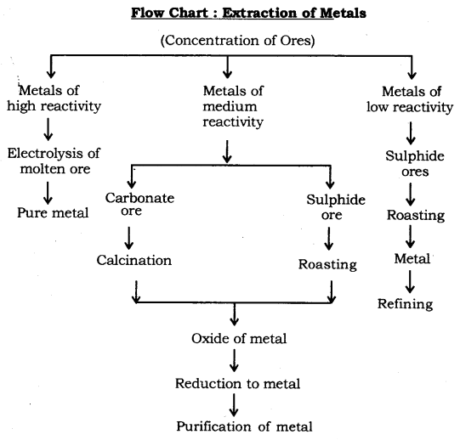
Event and Extraction of Metals: Minerals, ores, extraction of metals of least reactivity, extraction of metals of center reactivity, extraction of metals of high reactivity, refining or purifying metals, and erosion.
Event and Extraction of Metals:
Wellspring of metal: Metals happen in Earth’s outside and seawater; as ores. Earth’s hull is the significant wellspring of metal. Seawater contains numerous salts, for example, sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, and so forth.
Mineral: Minerals are normally occurring substances which have a uniform creation.
Ores: The minerals from which a metal can be productively extricated are called Ores.
Metals found at the base of reactivity arrangements are least reactive, and they are regularly found in nature in free-state, for example, gold, silver, copper, and so on. Copper and silver are likewise found as sulphide and oxide ores.
Metals found in reactivity arrangement, for example, Zn, Fe, Pb, and so forth, are generally found as oxides, sulphides or carbonates.
Metals found at the head of the reactivity arrangement are never found in free-state as they are reactive, model; K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al, and so forth.
Numerous metals are found as oxides since oxygen is plentiful in nature and is extremely reactive.
Extraction of Metals: Metals can be classified into three sections based on their reactivity: Most reactive, medium reactive, and least reactive.
The three significant advances engaged with the extraction of a metal from its mineral are:
- Fixation or advancement of ores.
- Transformation of the amassed mineral into unrefined metal and,
- Refining of impure or rough metal.