Digestion and Absorption: Class 11 Biology NCERT Chapter 16

Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 – Digestion and Absorption
In chapter 15 of NCERT class 11 Biology: Plants Growth and Development, You learnt about in all living organisms, growth is generally referred to as an irreversible increase in the size, the number of cells, and the whole organism. In this chapter: Digestion and Absorption, you will study that digestion is one of the most perplexing procedures that happen in our bodies. Let us learn a lot all the more intriguing realities about digestion and retention.
Did you realize that an individual on normal eats around 500 kgs of food in a year! Would you be able to envision how complicated and profoundly working our digestive system is to process this food?
Characterize and talk about – digestion.List – the properties of the nutritious trench , the pieces of the human digestive system. Talk about the job of digestive enzymesDefine digestion, Discuss mouth, portions of buccal pit – sense of taste, teeth, tongue.discuss-ingestion of food, teeth dependent on – homodont, heterodont, shrewdness teeth, transitory teeth deciduous teeth and dental formula.describe tongue and its job in digestion.introduce – Small digestive system, examine locales of small digestive system – duodenum, jejunum and ileum,Discuss – digestive juices got by little intestine,villi, lacteal, transformations of ileum for retention of processed food.discuss – Large digestive system, parts – cecum, colon and rectum, elements of internal organ, crap, defecation.
Quick revision notes
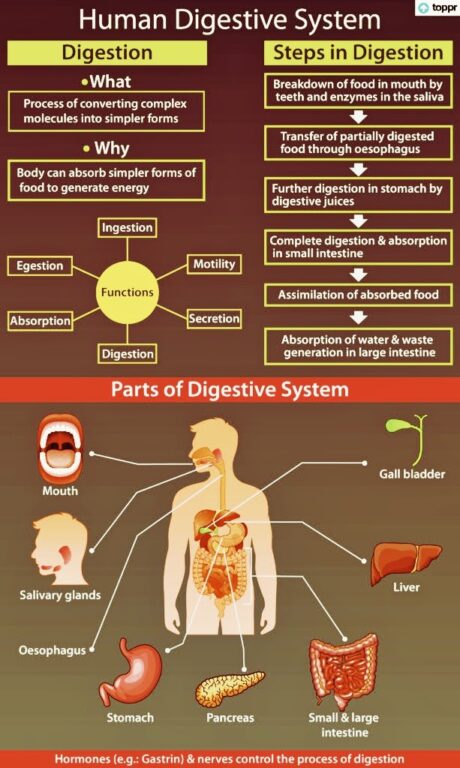
Human Digestive System
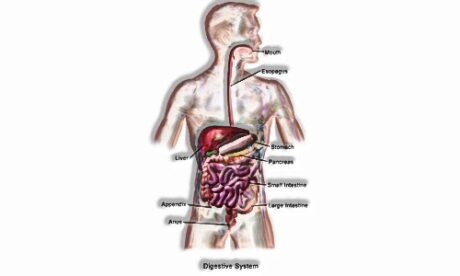
In Human digestive system, there are numerous parts that cooperate. The food that you eat has biomacromolecules, which are only the starches, (for example, sugars), proteins, lipids, (for example, fats), and nucleic acids. These must be changed over to their more straightforward structures with the goal that your body can assimilate it. These biomacromolecules are the structure hinders that you require to keep up your body, which is likewise made of these enormous organic particles, alongside water!
Therefore, this procedure of changing over complex food substances (atoms) into less complex structures to encourage retention is called Digestion. In humans, this system comprises of numerous parts and organs, including the wholesome channel, digestive organs, and a couple of adornment organs, for example, the teeth, salivary organs, tongue, pancreas, liver, gallbladder and so on.
By the by, the beginning stage where digestion really begins in the mouth! From the mouth, it goes through the wholesome channel, which is likewise called the gastrointestinal lot. This parcel comprises of the pharynx, throat, stomach, small digestive tract, internal organ, and rear-end. The mouth can be considered as the front opening of the wholesome waterway, while the rear-end is the back opening.
Browse more Topics under Digestion And Absorption
- Digestive System
- Process of Digestion
- Absorption and Assimilation
- Disorders of Digestive System
Digestive System Process:
From the Mouth to the Large Intestine and Anus. The Human digestive system process can be divided into stages, namely:
- Ingestion
- Motility
- Secretion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Excretion
The entire procedure begins in the oral hole, where the spit from the salivary organs blends in with the food and begins to start the breakdown of food. From the mouth, the food goes to the empty cylinder like organ the esophagus. Henceforth from the esophagus, food at that point goes to the stomach, where it separates further with the assistance of the acids and ground-breaking catalysts discharged by the stomach.
This semi-processed food at that point makes a trip down to the small intestine, where discharges from the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas further follow up on the food particles. The small intestine is partitioned into three sections called the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The majority of the digestion happens here in the small intestine, where ingestion likewise happens. When the greater part of the retention of water and processed supplements is finished in the small intestine, the staying waste items move to the internal organ. The digestive organ partitions into informative supplement, caecum, colon, and rectum. The fecal issue from the digestive organ comes out through the rear-end.
Digestive System Parts:
Mouth
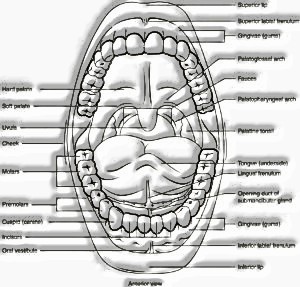
The anterior opening of the alimentary canal is the mouth. It leads to a buccal cavity or oral cavity, where teeth, tongue and salivary glands are present. Here, ingestion, mastication, and swallowing of food occur. In humans, there are a total of 32 permanent teeth. Since, there are four different types of teeth, namely, incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. These help in the chewing of food.
Salivary Glands
They are exocrine glands that produce salivation in the oral pit. They discharge a protein called amylase, which helps in the breakdown of starch into maltose. There are three sorts of salivary glands, to be specific:
- Parotid gland
- Submandibular gland
- Sublingual gland
- Stomach
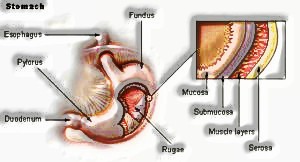
The esophagus prompts a sac-like organ called the stomach. It is a strong, empty organ, having a limit of 1 liter. The stomach holds food and furthermore is a blender and processor. It secretes solid acids and ground-breaking chemicals that help during the time spent separating of food. Food is by and large in a fluid or glues consistency when it leaves the stomach.
(Digestion and Absorption: Class 11 Biology)
Small Intestine
The small intestine is a long cylinder, which freely loops in the mid-region territory. Here, proteins from the pancreas and liver further separate the food. Three fragments make up the small intestines, which are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The compressions of the small intestine help in the development of food, alongside its breakdown, in the wake of blending in with the digestive discharges. The jejunum and ileum regions of the small intestine are answerable for the assimilation of food into the blood, however their villi.
Pancreas, Liver and Gall Bladder
These organs additionally assume a critical job in the human digestive system. The pancreas secretes catalysts that help in the breakdown protein, fat, and starch. The liver secretes bile and scrubs and filters the blood originating from the small intestine. The gallbladder stores the bile that the liver produces. It discharges bile into the small intestine to help in the digestion procedure.
Large Intestine
The large intestine is a long solid cylinder that has various parts, which are cecum, colon, and rectum. The waste that is left over after digestion of food, arrives at the rectum through the peristaltic developments of the colon.
Digestive System Controls
Hormones and nerves control the human digestive system. The dividers of the wholesome waterway have numerous sensors which manage the digestive capacities. Indeed, even hormones are engaged with the digestion procedure. The principle digestive hormone, gastrin is emitted in light of the nearness of food. Gastrin again animates the gastric corrosive discharge. All these control the digestion procedure.
Questions
Q: What is digestion?
Ans. Digestion is the way toward changing over complex food substances (atoms) into more straightforward structures to encourage assimilation.
Q: What are the different organs and parts related with the Human Digestive System?
Ans. The Digestive System in humans begins with the mouth or oral pit, prompting the nutritious channel. The nutritious channel comprises of the accompanying – pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and butt. The small intestine separates into three sections in particular, the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, while the large intestine isolates into a supplement, caecum, colon, and rectum. The liver, gallbladder, pancreas, teeth, salivary glands, tongue, and so forth likewise have a task to carry out in the digestive system.

