The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings:Class 6 Science NCERT Chapter 9

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 6 Science Chapter 9 – The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
In the previous chapter 8: Body movements,you have studied about how our body moves and its working.In this chapter 9: The living organisms and their surroundings you will study about the habitat and characteristics of living organisms.
Quick revision notes
Aquatic habitat
When creatures live in water, this spot of living is known as aquatic habitat.
Lakes, lakes, streams, seas, and so on., are instances of aquatic habitat.
Water is a medium in aquatic habitat.
Terrestrial habitat
When living beings live ashore, this spot of living is known as terrestrial habitat.
Woodlands, deserts, plantations, tea nurseries and mountains are the instances of terrestrial habitat.
Air is the medium in terrestrial habitat.
Mountain
The mountain is an exceptional terrestrial habitat where temperature is low and the majority of the territories are secured with day off.
The plants like grasses, greeneries and lichens and creatures like snow bear, fox, water fowl, musk deer and wolf are found generally in this habitat.
Some plants and creatures may have a similar habitat.
Adaptation: The difference in specific highlights and propensities, which empowers a plant or a creature to live in a specific habitat is called adaptation.
(Chapter 9: The living organisms and their surroundings)
Components of a habitat
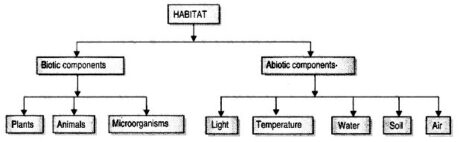
Light
The daylight is fundamental for the endurance of the biotic components as the sun is a definitive wellspring of vitality for every single living thing.
The daylight influences development, blossoming, seed germination and from numerous points of view in plants. Indoor plants put in the shade for quite a while become quicker yet gotten sensitive and frail.
Light likewise influences creatures. Creatures living in caverns and tunnels where daylight can’t reach have especially diminished eyes e.g., Proteus. Amblyopsis don’t have eyes.
Nighttime creatures: Some creatures like bats, cockroaches and owls are called nighttime as they are dynamic during night.
Temperature
Temperature directs development, development, generation, morphology and different parts of life.
Creatures living in hot territories e.g., snakes, desert rodents and reptiles can’t get adequate water. They have toughness and don’t perspire.
Desert creatures e.g., camel have long legs. Long legs help them to lift their body over the ground. Along these lines, they can maintain a strategic distance from direct contact with the hot ground.
Water
Every single living life form need water for their endurance.
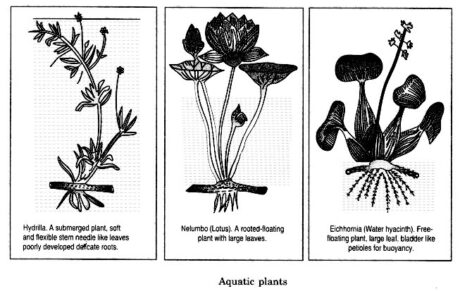
Aquatic plants: These have the accompanying adaptations:
Root system is ineffectively evolved.
Air filled depressions discovered inside the body make them elastic and light.
Leaves in lowered plants are slender and tight; while in gliding plants, they are huge and level with waxy covering.
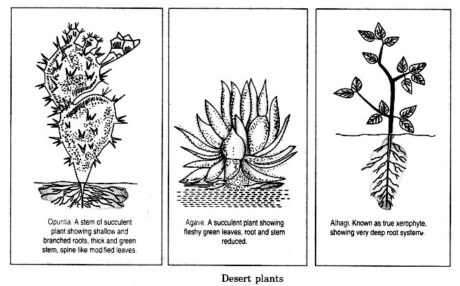
Desert plants: These have the accompanying adaptations:
Very much created root systems.
Stem is delicious and light which help away of water. It is additionally green and performs photosynthesis.
Stomata (depressed) are less in number.
Leaves are either little or changed over into spines.
Fish: It has the accompanying adaptation:
Tightening closes.
Elusive scales which help in swimming.
Gills for breath.
Phytoplanktons: These are drifting plants, in aquatic habitat.
Zooplankton: These are little creatures drifting on the outside of aquatic habitat.
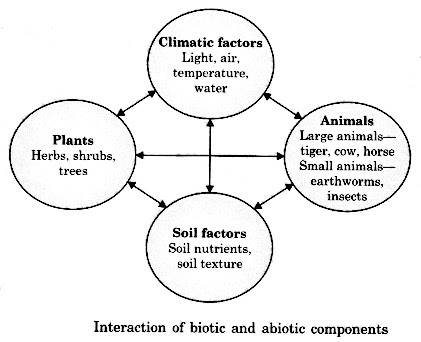
Connection of biotic and abiotic components: Organisms don’t live in disconnection however are reliant.
Living things: These are the items which need water, air and supplements for their endurance.
Non-living things: These are the items which needn’t bother with water, air and supplements for their endurance.
Cell: It is the essential basic and useful unit of the living things. The structure of a cell can be found in the strip of an onion bulb or from the lower surface of a leaf under a magnifying glass or a magnifying instrument.
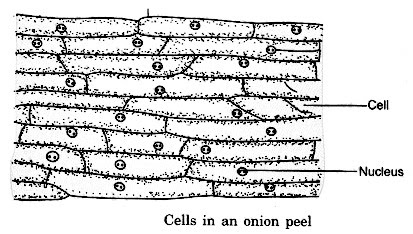
Life: It is a procedure seen uniquely in living articles as development, development, taking care of or eating, affectability, breath, discharge and generation.
Attributes of the living things: All living things on this planet have certain fundamental qualities. These incorporate the accompanying:
- Growth
- Movement
- Feeding
- Responsiveness
- Excretion
- Respiration
- Cellular structure
- Reproduction
- Adaptation.
Growth: It is characterized as the perpetual irreversible increment in the size and all out weight of the living item.
- Creatures develop for a specific period.
- If there should be an occurrence of trees, development happens for the duration of the life.
- Development in plants and creatures is impacted by a few elements like food, atmosphere, life style, and so forth.
Life Span: Each creature lives for a specific period. This period is alluded to as life range.
Movement: Change in the situation from one spot to other is called development.
- Locomotion: The development including change of spot in creatures is called Locomotion.
- Creatures use wings (feathered creature), balances (fish), appendages (dairy animals, horse, wild ox, man) for velocity.
- Plants for the most part show developments of different parts, e.g., bloom buds open, roots become away from light, when we contact the leaves of mimosa (contact me not), they shrink up.
Cellular Structure
- Cells comprise plants and creature bodies.
- Cells are composed in different manners in different creatures.
- They help in doing different capacities like nourishment, breath, and so on.
- They are called basic and practical unit of every single living being.
Nutrition: The way toward taking food by life forms is for the most part alluded to as sustenance or sustenance.
- Food and water are essential to sustain life.
- Food gives vitality that helps in the development of body and its fix.
- Autotrophs: They are the living structures which can integrate their own food by photosynthesis, e.g., green plants.
- Heterotrophs: They are the living life forms which can’t produce their own food, e.g., all creatures.
- Saprophytes: The living life forms which acquire their nourishment from the dead plants and creatures are called saprophytes.
- Parasites: The plants and creatures that feed on the other living bodies are called parasites.
Respiration
- Respiration is a procedure where oxygen taken by a living being consolidates with saved food, experiences oxidation and discharges vitality.
- Breathing: Taking in air and discharging it in creatures is alluded to as relaxing.
- We breathe in oxygen (O2) and breathe out carbon dioxide (CO2).
Excretion
- The expulsion of excretory waste from the body of a living being is called discharge.
- The procedure of expulsion of squanders in plants is alluded to as discharge.
- Latex, gum and gum are squanders for the plant yet valuable for us.
Response to Stimuli
- Living creatures react to changes in their environmental factors.
- Boosts: The elements like food, water, light, contact, gravitational power, and so forth., are upgrades (improvement) to which plants and creatures react.
Reproduction
- The procedure of a living being to create of its own sort is called reproduction.
- Life produces life.Plants duplicate through seeds. A few plants additionally repeat through vegetative parts.
- Adaptation: The adjustment in specific highlights and propensities which empower a plant or a creature to live in a specific habitat is called adaptation.
- Aquatic habitat: When life forms live in water, their place of living is known as aquatic habitat.
- Biotic segment: Living things of a habitat structure its biotic segment.
- Discharge: The expulsion of nitrogeneous squander substances from the body of a living being is called discharge.
- Development: Increase in size and absolute load of the living being is called development.
- Habitat: where a life form endures, prospers and recreates is called its habitat.
- Living things: These are the things which need water, air and supplements for their endurance.
- Proliferation: The procedure of a living being to deliver of its own sort is called generation.
- Breath: Respiration is a procedure wherein air taken by a life form consolidates with the held food, experiences oxidation and discharges vitality.
- Upgrade: The components like food, water, light, contact, gravitational power, and so forth., are boosts to which plants and creatures react.
(Chapter 9: The living organisms and their surroundings)

