Respiration in Organisms: Class 7 Science NCERT Chapter 10

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 – Respiration in Organisms
In the previous chapter 9, you learned about Soil. In this chapter you will learn about Respiration in Organisms.
Quick revision notes
Every cell of an organism performs capacities like sustenance, transport, discharge and reproduction for this reason, it needs vitality. Our food is put away vitality which is delivered during breath. Breathing is the cycle during which, we take in air having oxygen and we inhale out air wealthy in carbon dioxide. The air wealthy in oxygen is moved to all pieces of the body and at last to every cell. This oxygen is used by the cell for breath. Tbe cycle of breakdown of food in the phones of an organism with the arrival of vitality is called cell breath.
Types of Respiration
On the basis of the presence or absence of oxygen, respiration is classified into two types:
- Aerobic Respiration
At the point when the breakdown of glucose happens with the utilization of oxygen, it is called vigorous breath. During high-impact breath, glucose is totally separated into carbon dioxide and water and vitality is delivered. High-impact breath happens in mitochondria.
It can be shown by the following equation:
Glucose(food) Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Aerobic respiration is seen in most of the organisms such as humans (man), dogs, cats, lions, elephants, cows, buffaloes, goats, snakes, earthworms, frogs, fishes, etc.
- Anaerobic Respiration
At the point when a breakdown of glucose happens without utilizing oxygen, it is called anaerobic breath. The glucose isn’t totally separated into carbon dioxide and water. A middle compound is framed with the arrival of less measure of vitality during this cycle. It very well may be appeared as follows:
Glucose Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
Yeasts, for example, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and certain microscopic organisms do anaerobic breath. These organisms that do breath without oxygen are called anaerobes.
Yeast is a solitary celled organism. During anaerobic breath (additionally called aging), yeast produces ethanol or liquor as a result which is utilized in making wine and lager. The carbon dioxide created by yeast is utilized in the bread making industry. The C02 gas delivered during this cycle makes the bread batter rise.
Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles
Generally, high-impact breath happens in people, yet under specific conditions, anaerobic breath may likewise happen in our muscles for a brief timeframe, because of impermanent insufficiency of oxygen. At the point when we play out a substantial exercise like running, cycling, strolling, weight lifting, and so forth., we require a lot of vitality. To meet the vitality necessity our muscle cells perform anaerobically. breath. During this cycle, the glucose or food in the muscle cells is incompletely separated without oxygen to frame lactic corrosive and some additional vitality is delivered.
The following equation shows the production of lactic acid:
Glucose(Food) Lactic acid + Energy
This our own on the grounds that during energetic physical movement, the use of oxygen our own at a quicker rate in the muscles that can be provided by the blood.
At the point when the lactic corrosive delivered during anaerobic breath, gets aggregated in the muscles, it causes muscle cramps. The muscle issues can be assuaged by cleaning up or a back rub. This improves the dissemination of blood and oxygen gracefully to the muscle cells increments. The expanded flexibly of oxygen brings about the total breakdown of lactic corrosive into carbon dioxide and water, accordingly giving help from cramps.
Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| It occurs in the presence of oxygen. | It takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| The complete breakdown of food takes place in aerobic respiration. | Partial breakdown of food occurs in anaerobic respiration. |
| End products of aerobic respiration are CO2 and water. | End products of anaerobic respiration are alcohol and CO2 or lactic acid (in muscles). |
| A large amount of energy is produced during aerobic respiration. | Less amount of energy is produced during anaerobic respiration. |
Breathing
It is the cycle wherein air wealthy in oxygen is taken inside and air wealthy in CO2 is given out, with the assistance of respiratory organs. In this way, breathing includes two stages which occur then again.
- Inhale breath: Taking in of air wealthy in oxygen into our body is called inward breath.
- Exhalation: Giving out air wealthy in carbon dioxide from our body to the outer condition is called exhalation.
This movement must be performed under the management of your instructor or parent. Close your noses and mouth firmly and take a gander at a watch. Note down the ideal opportunity for which you could hold your breath. We will before long beginning inclination uncomfortable and can’t hold our breath for even one moment.
Breathing Rate
The occasions an individual takes in a moment is named as breathing rate. A grown-up individual can breathe in and breathe out 15-18 times in a moment. It is the normal breathing pace of a grown-up individual.
The breathing pace of an individual isn’t generally steady. It changes as per the oxygen prerequisite of the body. Breathing rate is fairly quicker in ladies than in men and in kids, it is higher (20-30 times/min) than grown-ups. Breathing rate is slowest while dozing (as less vitality is required) while greatest during hefty exercise like running, weight lifting, and so on (much vitality is required). Expanded breathing rate gives a more prominent measure of air section into the lungs, subsequently blood can ingest oxygen at a quicker rate. Quicker breathing supplies more oxygen to the body cell for creating more vitality, required for substantial activities.
During substantial exercise, the breathing rate can increment to 25 times each moment. Along these lines, food gets separated at a quicker rate and consequently cause us to feel hungry.
At the point when we feel tired, sluggish or tired, we yawn (for example open our mouth wide to take a long and full breath, of air), in light of the fact that our breathing rate eases back down and the body doesn’t get adequate oxygen.
Component of Breathing
-
- The component of breathing can be perceived by the accompanying focuses:
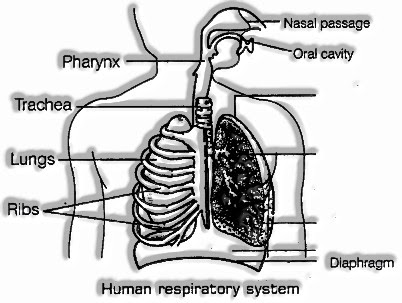
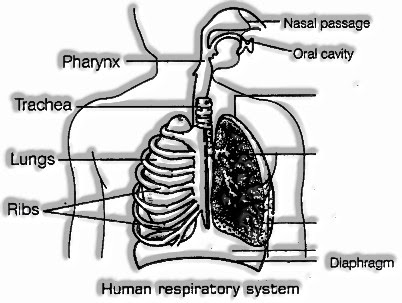
- Typically, we take in air through our noses. At the point when we breathe in air, it goes through our noses into the nasal hole.
- From the nasal pit, the air arrives at our lungs through the windpipe.
- Lungs are available in the chest pit. This depression is encircled by ribs on the sides.
- A huge, solid sheet called stomach shapes the floor of the chest pit.
Smoking
Lungs are fragile organs and fundamental for breathing, in this way signaling us alive. Smoking tobacco as beedi, cigarette or stogie harms our lungs continuously and causes sick wellbeing. While smoking, smoke alongside synthetics present in tobacco enters our body. These synthetics present in tobacco harms the lungs from numerous points of view like breathing becomes troublesome causes cellular breakdown in the lungs, heart illnesses, and so on. Smoking additionally influences individuals around smokers as they likewise breathe in air containing tobacco. This is called inactive smoking.
The instrument of breathing includes the development of the stomach and ribcage. The total cycle of breathing can be talked about as follows:
Breathing In or Inhalation
At the point when we breath air in (or breathe in) two cycles happen together, for example the muscles between the ribs contract causing the ribcage to move upward and outward, while the stomach agreements and moves downwards. This upward and descending development of ribcage and stomach individually builds the space in the chest cavity and makes it bigger. As the chest depression increases, it sucks air from outside the lungs and lungs get topped off with air and grow.
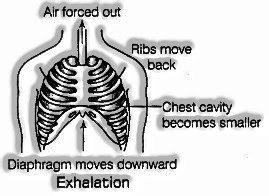
Breathing Out or Exhalation
At the point when we breath let some circulation into or breathe out the converse cycle happens, for example the muscles of the ribs discharge causing the ribcage to move descending and internal, while stomach deliveries and moves upward. This descending development of the rib confine and upward development of stomach diminishes the space in our chest cavity and makes it littler. At the point when the chest cavity decreases, the air is pushed out of the lungs.
Sneezing
The air we breathe in contains different kinds of undesirable particles like smoke, dust, dust, and so on. Their particles are allergens. During inward breath, these particles get caught in the hair present in our nasal pit. They cause aggravation in the covering of the nasal cavity, because of which we sniffle. Sniffling ousts the unfamiliar particles from the breathed in air so sans dust, clean air may go into the lungs.
We should fare thee well while wheezing in that we should cover our nose so unfamiliar particles ousted during sniffling may not be breathed in by someone else close by us.
Breathed out Air Contains Carbon Dioxide
The air is a blend of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water fume, and so on. The distinction between breathed in air and breathed out air is that the breathed in air contains more oxygen while breathed out air contains more carbon dioxide. Other than oxygen and carbon dioxide, the air additionally contains more water fume. Breathed out air contains more water fume than the breathed in air.
The air which we inhale and exhale is a mixture of gases and water vapours. The inhaled air is rich in oxygen while exhaled air is rich in carbon dioxide. The percentage of O2 and CO2 in inhaled and exhaled air can be shown as follows:
| Percentage of O2 | Percentage of CO2 | |
| Inhaled air | 21% | 0.04% |
| Exhaled air | 16.4% | 4.4% |
Breathing in Other Animals
Various creatures have various organs for the trading of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Creatures, for example, elephants, lions, dairy animals, goats, frogs, reptiles, snakes, fowls have lungs in their chest depressions like people for breath. The littler creatures like cockroaches, night crawlers, fishes, ants and mosquitoes don’t have lungs. Subsequently, breath in these creatures happens by different methods.
Cockroach
Creepy crawlies like the cockroach, grasshopper, and so forth., have little gaps on the sides of their body. Their openings are called spiracles. The spiracles on the assortment of bugs are associated with a system of slender air tubes called tracheae which; spreads into the entire body of the creepy crawly, where the trading of gases happens. Air wealthy in oxygen races through spiracles into the tracheal cylinders, diffuses into the body tissue and arrives at each cell of body. Thus, CO2 from the cells goes into tracheal cylinders and moves out through spiracles.
The blood in these creatures don’t contain hemoglobin and isn’t red in shading. They can’t convey oxygen to all the pieces of the body. In this manner, transport of air happens through the spiracles in these organisms. The tracheal system or spiracles are just found in bugs, in no other gathering of creatures.
Earthworm
Earthworm and parasites assimilate the climatic oxygen through their clammy and vile skin since gases can without much of a stretch go through the sodden and disgusting skin. They retain the barometrical oxygen through their wet skin and transport it through the blood to all the cells.
Frog
A frog-like human has a couple of lungs yet when they are in the water, they inhale through their sodden and tricky skin. At the point when they are ashore they inhale through their noses and a couple of lungs.
Breathing Under Water
There are numerous organisms which live in water. They do likewise inhale submerged. Some of them given underneath:
Fish
Fishes are the sea-going creatures that live in water. These have an exceptional organ for breathing called gills. The oxygen broke up in water enters through the gills. Gills are really the projections of skin and have veins for the trading of respiratory gases. The fishes inhale by taking in water through its mouth and sending it over the gills. The oxygen broke up in the water is extricated by the gills and the removed oxygen is consumed by the blood.
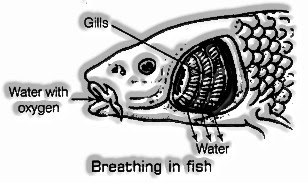
This oxygen is then carried to all the parts of fishes for respiration. The carbon dioxide produced during respiration is brought back by the blood into the gills and expelled into the surrounding water.
Dolphins and Whales
Ocean creatures like dolphins and whales live in water however not at all like fishes, they don’t have gills for breath. These have nostrils which are called blowholes. Their blowholes are situated on the upper pieces of their heads. These creatures take in through their noses and lungs. Dolphins and whales rise to the top of ocean water now and again to take in air, once in a while whales discharge a component of water that moves upwards like a shower. This is on the grounds that when a whale inhales ventilate of its blowhole it shows up as a shower or fog, additionally called a spot. It very well may be seen from numerous miles away. Blowholes are encircled by muscles that keep the gaps shut when the whales or dolphins are submerged and open it when the creature is at the surface and needs to relax.
The human can’t endure submerged on the grounds that they don’t have any gills to utilize oxygen broke down in water for relaxing. At the point when we go submerged we need to take oxygen gas chambers for relaxing.
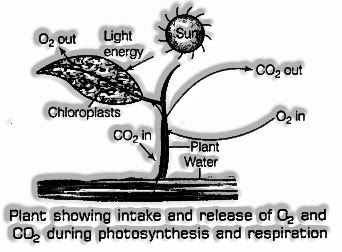
Breath in Plants
All the organism on the planet breathes whether it is a creature or a plant. Plants likewise take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. They additionally breakdown glucose into C02 and water and deliveries vitality to perform different capacities. The breath in plants varies from the creature on the grounds that in plants, breath happens through leaves and roots, and so on. They do breath freely, for example each plant part can autonomously take in oxygen from the air, use it to acquire vitality and give out CO2.
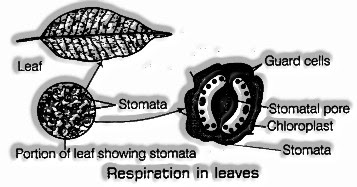
Breath in Leaves
The leaves of the plants have little pores on their surface which are called stomata. The trading of gases, for example O2 and CO2 in the leaves happens through stomata during breath. The oxygen from air goes into a leaf through stomata and ranges inside all the phones of the leaf through dissemination while CO2 created during breath likewise diffuses from the leaf to the air through the stomata.
Respiration in Roots
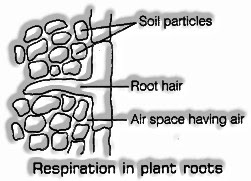
Root cells of the plants breathe under the ground. They additionally need oxygen to do breath and deliveries vitality for their own utilization. Root cells get oxygen from the air present in the spaces between the dirt particles.
Plant roots have an enormous number of minuscule hairs on them which are called root hairs. Oxygen from the air present in soil particles diffuses into root hair and scopes to the cells of the root where it is used for breath.
Note: If a pruned plant is over watered for quite a while, the plants pass on. This is on the grounds that the water atoms occupy the space between soil particles and push the freshen up. Because of this explanation, the oxygen isn’t accessible to the roots for vigorous breath and plants kick the bucket. Because of the creation of alcoholic items because of going through anaerobic breath. It isn’t astute to rest under a tree during the night in light of the fact that in the night, plants don’t photosynthesis and plants can’t utilize CO2. Along these lines, an individual will experience the ill effects of suffocation and feel the overabundance weight on the chest.
Exchange of Gases
The trading of gases happens in the plants constantly, however it is expanded during day time. The leaves are all the more effectively associated with photosynthesis during the day time within the sight of daylight. The CO2 delivered during breath is used by the plant during photosynthesis to create its food.
During photosynthesis, the O2 is delivered by plants which are taken up during breath in plants. Along these lines, a harmony somewhere in the range of CO2 and O2 is kept up by the plants.
Breath accordingly gives ceaseless vitality to plants to play out the entirety of its capacities paying little heed to time.