Reproduction in Organisms: Class 12 Biology NCERT Chapter 1

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 – Reproduction in Organisms
In this chapter, you will get to know about Reproduction. Reproduction is a particular trait of Living Organisms. Every single living being has endured and advanced throughout the hundreds of years by ethicalness of Reproduction. Living Organisms Reproduce and offer ascent to comparable organisms of similar species. Various organisms have various ways and procedures of Reproduction. In this part, we will find out about the sorts and procedures of Reproduction.
Kinds of Reproduction
Reproduction can be of two kinds:
Asexual-Involves, a solitary parent who offers ascend to another creature
Sexual-Involves two guardians of the other gender that offer ascent to another life form.
Quick Revision Notes
Reproduction is a natural procedure of the development of new offspring from the pre-existing living being. Reproduction turns into an essential procedure without which species can’t make due for long. It guarantees congruity of species age after age as more seasoned people experience senescence and eventually amazing.
Life expectancy – • The period from birth to the regular demise of a living being represents its life expectancy. The life expectancy of organisms shifts from not many days (Butterfly-1to fourteen days) to a great many years (Banyan tree).
Kinds of Reproduction:
In view of whether there is a couple of organisms participating during the time spent reproduction
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
At the point when single guardians create the posterity with or without the association of gamete arrangement, the reproduction is called asexual reproduction.
At the point when two guardians (other gender) take an interest in the reproduction process and furthermore includes the fusion of male and female gametes, it is called sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
Generally followed by organisms with moderately easier associations.
A single parent delivers offspring.
With/without the association of gamete arrangement.
Offsprings delivered are hereditarily and morphologically like one another, and to the parent, for example, they are clones.
- In Protista and Monera, the parent cells partition into two to offer ascent to new people. Subsequently, in these organisms, cell division is simply the method of reproduction.
- Binary splitting in this technique for asexual reproduction, a cell isolates into equal parts and quickly develops into a grown-up. Ex-single adaptable cell, paramecium.
- Budding–little buds are delivered that stay appended at first with guardians and get isolated on development. Ex. Yeast.
- Fungi and basic plants like green growth recreate through unique reproductive structures like zoospores (motile structure), conidia (Penicillium), buds (hydra), and gemmules (wipes).
- In plants, vegetative reproduction happens by vegetative propagules like sprinter, rhizome, sucker, tuber, counterbalance, and bulb.
WATER HYACINTH (Terror of Bengal)
One of the most obtrusive weeds
Develops any place there is standing water.
Channels oxygen from the water-prompts demise of fishes.
Presented in India in light of its pretty blossoms and state of leaves
Vegetative proliferation happens at an exceptional rate.
Asexual reproduction is the most widely recognized strategy for reproduction in organisms with less difficult bodies than in green growth and parasites. Yet, during the negative condition, they move to sexual reproduction.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION:
Includes the arrangement of male and female gametes by two people of the other gender.
Posterity is delivered by fusion of male and female gametes not indistinguishable from one another or to the guardians.
All sexually imitating organisms share a comparable example of reproduction.
- In sexual reproduction, the fusion of male and female gametes brings about posterity that are not indistinguishable from guardians.
Various PHASES IN SEXUAL REPRODUCTION:
- Juvenile stage – The period among birth and sexual development is called the juvenile stage. In plants, it is known as the vegetative phase. The end of the juvenile/vegetative stage denotes the start of the reproductive stage.
- Reproductive stage
- Some plants show blooming, specifically season and some different blossoms in all seasons. Some different plants like bamboo species blossom once in a lifetime (following 50-100 years), Strobilanthes kunthiana (neelakurinji), flowers once in 12 years.
- The female placental creatures show a cyclic change in exercise ovaries and accessory organs just as hormones during the reproductive stage.
Menstrual cycle
- It happens in monkeys, chimps, and individuals.
- Cycle comprises three stages: menstrual, proliferative, and secretory stage.
- Blood streams over the most recent couple of days of the cycle. The wrecked endometrium is dropped during the monthly cycle.
- Female doesn’t allow relations during the menstrual period of the cycle.
Oestrous cycle
- It happens in non-primates like cows, sheep, rodents, deer, canine, tiger, and so forth.
- It comprises a brief time of oestrous or warmth. It is 12-24 hours in the cow, followed by an anoestrous or inactive period.
- Blood doesn’t stream in this cycle. The messed up endometrium is reabsorbed.
- Female grants lovemaking just during the estrous period.
- Both in plants and creatures, hormones are answerable for the progress between various periods of the life cycle. Association among hormones and natural variables control the reproductive procedures.
- Senescent stage –
It is the finish of the reproductive stage.
Mature age at last prompts demise.
Occasions in Sexual Reproduction: Pre-preparation, Fertilization, Post-treatment
Pre-preparation, all the occasions preceding fusion of gametes are remembered for it. It incorporates gametogenesis and gamete moves.
- Gametogenesis is the procedure of development of male and female gametes. Gametes are haploid cells that might be comparative or disparate in structure. In green growth, the two gametes are comparative in a structure called homogametic (isogametes). In higher living beings that imitates sexually, two morphologically particular gametes are called heterogametes, male gametes are called antherozoid or sperm, and female gametes are called ovum or egg.
Isogametes. heterogametes
In growths and plants, homothallic and monoecious terms indicate the bisexual condition and heterothallic and dioecious are utilized for the unisexual condition. In blooming plants, the unisexual male blossom is staminate, i.e., bearing stamens, while the female is pistillate or bearing pistils.
- In creatures, species that have both male and female reproductive organs in the same individual are called bisexual or bisexuals (worm, wipes, tapeworm, and so on), and both have male or female reproductive organs are called unisexual (cockroach, human).
- Gametes are consistently haploid( having half arrangement of the chromosome ), even though organisms might be haploid and diploid. Diploid organisms structure gametes by meiotic division. The organisms having a place with green growth, parasites, and bryophytes have haploid plant body and pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms and a large portion of creatures are diploid ( having a twofold arrangement of a chromosome )
- In diploid organisms, the gamete mother cell (meiocyte) experiences meiosis in which one lot of chromosomes is present in gametes.
- Gamete Transfer – in a more significant part of organisms, male gametes are motile, and female gametes are non-motile, aside from parasites and green growth in which the two gametes are motile.
- In basic plants like green growth, organisms, bryophytes, and pteridophytes, water is the medium through which male and female gametes move. The quantity of male gametes is significantly more than the number of female gametes as a large portion of male gametes neglects to arrive at the female gametes.
- In higher plants, pollen grains are a transporter of male gametes, and ovule has eggs. Pollen grains must be moved from anther to stigma to encourage preparation. The exchange of pollen grains from the anther to stigma is called pollination. Pollination might act naturally (anther to the stigma of the same blossom) or cross (anther to the stigma of many flowers).
- Pollen grains sprout on stigma to create a pollen tube that conveys the male gametes close to the ovule.
- Treatment – The fusion of male and female gamete is called preparation or syngamy. It brings about the development of the diploid zygote.
- The procedure of improvement of new organisms without treatment of female gametes is called parthenogenesis. For instance bumble bee, rotifers, and reptiles
| EXTERNAL FERTILIZATION | INTERNAL FERTILIZATION |
| Syngamy happens outside the body of the living being. Large quantities of gametes are delivered in the encompassing medium.
Ex. Bony fishes and Amphibians. |
Syngamy happens inside the body of the living being Numbers of ova created are less. However, enormous quantities of male gametes are delivered, and they travel towards the ovum.
Ex. Birds and Mammals. |
Post-Fertilization Events- occasions in sexual reproduction after the arrangement of the zygote.
A zygote is the imperative connection that guarantees the congruity of species between organisms of one age and the following. Each sexually repeating living being, including people, starts life as a solitary cell–the zygote.
• In the organisms, having outer preparation, a zygote is shaped in the outside medium (water), and those having inner treatment zygote are framed inside the assemblage of the female.
• In green growth and parasites, zygote builds up a thick divider impervious to drying up and harm. This sprouts after a time of rest.
• In the organisms having a haplontic life cycle, zygote partitions shape haploid spores that grow to frame a haploid person.
Embryogenesis – the procedure of improvement of an incipient organism from the zygote. During this, zygote experiences mitotic division and cell separation. Cell division increments the number and cell separation help data of new gathering of cells and organs.
| Oviparous | Viviparous |
| The advancement of zygote happens outside the collection of organisms and lay fertilized or unfertilized eggs.
Ex – Reptiles and birds. |
The advancement of zygote happens inside the collection of organisms and produces youthful ones.
Ex- Human, dog, horse etc. |
•In blooming plants, a zygote is shaped inside the ovule. After treatment, sepals, petals, and stamens of blossom tumble off. The zygote forms into incipient organisms and ovules into seeds. The ovary forms into natural products which build up a thick divider called the pericarp, defensive in work.
• After dispersal, seeds develop under the positive condition to create new plants.
A couple of sorts of organic product demonstrating seeds (S) and defensive pericarp (P)
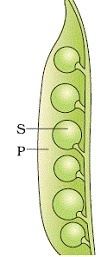
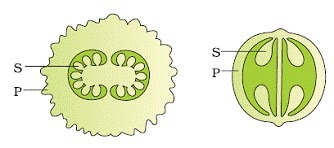
A few kinds of fruit showing seeds (S) and protective pericarp (P)
Questions
Ques. Which one is the female reproductive organ in a blooming plant known as?
- Ovaries
- Testicles
- Androecium
- Gynoecium
Answer: Option D Gynoecium. The female reproductive organ in a blooming plant is on the whole known as the gynoecium. It is made out of the stigma, style, ovary, and ovules.

