Panchayati Raj: Class 6 Civics NCERT Chapter 5

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 6 Civics Chapter 5 Panchayati Raj
In the previous chapter 4: Key Elements Of A Democratic Government, We studied that democracy is a rule by the people of the country. So, people themselves run the country by participating in the making of these rules. What is Panchayati Raj? How do systems in villages work? Here, you will learn all this and more from Class 6 Civics Chapter 5 “Panchayati Raj” from the book “Social and Political Life”.
Quick revision notes
Gram Sabha
A meeting of all adults who live within the same region in the area of a Panchayat is called Gram Sabha. Subsequently, it covers an area of one village or at times, altogether a few villages. Someone who is 18 years old or older and holds the right to vote can be a member of the Gram Sabha. So, the meeting starts with the Panchayat President (Sarpanch) and the other members (the Panchs) expressing their thoughts, opinions, and plans.
In every village, separation of panchayat is into wards in smaller areas. In each ward, they choose a representative who is the Ward Member (Panch). The Gram Sabha is a prominent body of the Panchayati Raj System. Consequently, it is accountable for strategizing the growth of the village and ensures the basic amenities of village people. The Gram Panchayat generates its fund by collecting taxes on houses, market places, government scheme funds, and donations, etc.
In a Gram Sabha, all the members also make a decision for a Sarpanch who is known as the Panchayat President. Firstly, the ward Panchs and the Sarpanch are elected for 5 years and they shape the Gram Panchyat. The secretary of the Gram Panchayat also becomes the Secretary of the Gram Sabha. However, the secretary is appointed by the government authorities for collecting the meeting of the Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat and maintaining a file of the proceedings.
In the Gram Sabha, all the work of the Gram Panchayat is for the people. The Gram Sabha blocks or prevents the Gram Panchayat from taking false actions like corruption or misusing cash or biases in decisions. Moreover, It ensures to retain and record actions on the elected representatives and makes them responsible for their actions.
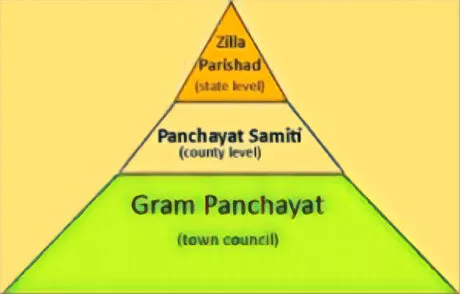
The Panchayati Raj System is a body in which individuals take part in their own government. The first tier or level of democratic government is the Panchayati Raj System. Further, it extends to two other levels – first, District Panchayat or the Zila Parishad, and second, the Janpad Panchayat or the Panchayat Samiti.
Three Levels of Panchayats
Panchayati Raj System is a procedure through which individuals take an interest in their own administration. In rural zones, the Gram Panchayat-first tier or level of democratic government. The Panch and the Gram Panchayat- accountable to the Gram Sabha- are the individuals from the Gram Sabha who chose them. People’s interest in the Panchayati Raj framework stretches out to two different levels. One is the Block level, known as the Janpad Panchayat or the Panchayat Samiti and there are Gram Panchayats under it.
Over the Panchayat Samiti is the District Panchayat or the Zila Parishad that really makes formative arrangements at the regional level. With the assistance of Panchayat Samitis directs the funds dissemination among all the Gram Panchayats. Each state in the nation has its own laws as to Panchayats. The thought is to give increasingly more space for individuals to take an interest and speak loudly.
Extra Notes
Progression of Panchayati Raj framework
As we saw that panchayat framework fills in as different Ward Sabha or Gram Sabha. However, this Gram Sabha is going by the Gaon Panchayat at the town level and cares for the town level duties.
At that point, we have Anchalik/Janpad/Block or Panchayat Samiti at the square level. At the square level, we have a BDO official who takes care of a gathering of towns.
Panchayat
For instance, let say if the district is having 10 towns and each one of those 10 towns is taken care of by the Block Development Officer who is accountable for all these 10 towns and all these 10-gram panchayats are responsible to the Panchayat Samiti.
Lastly, we have Zilla Parishad at the locale level. All the Block Development Officers are liable to the Zilla Parishad or the body at the area level. The Zilla Parishad really makes the formative arrangement at the locale level with the assistance of Panchayat Samiti.
In light of the Indian Constitution, this panchayat has its own laws. The fundamental thought is to give increasingly more space for individuals to partake and speak more loudly in the towns to acquire advancement in the nation.
Questions
Q1. State the primary elements of Gram Panchayat?
Ans: Main elements of the Gram Panchayat are:
Upkeep and development of water assets, streets, waste, School structures and CPR (normal property assets).
Duty and gather neighborhood charges. Execute government plans identified with business.
Q2. Name the three degrees of the Panchayat.
Ans: The three levels are:
Gram Panchayat at the town level
Square Level – Anchalik/ Janpad / Block or Panchayat Samiti
District level – Zilla Parishad