Our Country – India:Class 6 Geography NCERT Chapter 7

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 6 Geography Chapter 7 – Our Country India
In the previous chapter 6: Major landform of earth we have studied about the different landforms. In this chapter 7: Our Country India we will study about major physical division of our country.
Quick revision notes
India in the North is limited by the Himalayas, the Arabian Sea in the West, the Bay of Bengal in the East and the Indian Ocean in the South.
India has a territory of about 3.28 million sq. km.
The North-South degree from Kashmir to Kanyakumari is around 3,200 km. Subsequently, the west degree from Arunachal Pradesh to Kuchchh is around 2900 km.
Locational Setting
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ N) goes practically partially through the nation.
- From South to North. India reaches out between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N scopes.
- From West to East, India reaches out between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E longitudes.
- The neighborhood time changes by four minutes for each one level of longitude.
- The neighborhood season of longitude of 82°30′ E has been taken as the Indian Standard Time.
India’s Neighbours
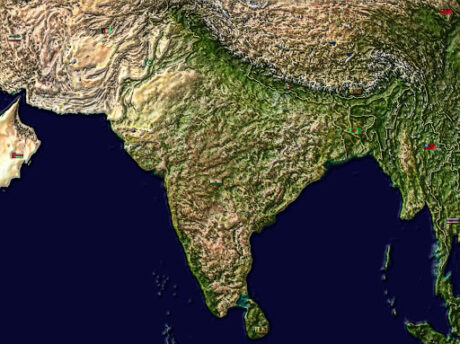
- There are seven nations that offer land limits with India.
- The seven nations are Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan. Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Island neighbors are Sri Lanka and the Maldives.
- The Palk Strait Isolates Sri Lanka from India.
(Chapter 7: Our Country India)
Political and Administrative Divisions
- India is separated into 29 states and 7 association regions.
- Delhi is the public capital.
- Rajasthan is the biggest state and Goa is the littlest state regarding territory.
- Physical Divisions
- The Himalayas in the North are separated into three fundamental equal reaches.
- The three principle equal extents are Great Himalaya or Himadri, Middle Himalaya or Himachal and Shiwalik.
- The Northern Indian fields lie toward the South of the Himalayas.
- In the Western piece of India lies the Great Indian desert.
- Toward the South of Northern fields lies the peninsular level.
- Aravali Hills is perhaps the most established scope of the world.
- The Western Ghats or Sahyadris outskirt the level in the West and the Eastern Ghats give the Eastern limit.
- Toward the West of the Western Ghats and the East of Eastern Ghats lie the waterfront fields.
- The streams Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri channel into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Ganga and Brahmaputra stream into the Bay of Bengal framing the Sunderban Delta.
- Lakshadweep Islands are situated in the Arabian Sea.
- The Andaman and the Nicobar Islands lie toward the South-East of the Indian terrain.
Our nation, India is immense. It has a zone of about 3.28 million sq. km. In the north, it is encircled by the Himalayas; in the west; there is the Arabian Sea; in the east; the Bay of Bengal and in the south; the Indian Ocean.
India has various landforms—the grand mountains, the Great Indian Desert, the Northern fields, the lopsided level, and the coasts and islands.
The atmosphere of India additionally changes from district to locale.
We additionally discover decent variety in greenery just as in language and culture.
India is the second most crowded nation of the world after China.
India is situated in the Northern half of the globe. The Tropic of Cancer goes through it.
The sun rises two hours sooner in the east, for example Arunachal Pradesh than in the west i.e, Gujarat.
India’s seven neighboring nations are—Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Afghanistan.
The Palk Strait isolates Sri Lanka from India
India is partitioned into 28 states and 7 Union Territories. Delhi is the public capital.
Rajasthan is the biggest state while Goa is the littlest state regarding zone.
India has various physical highlights—mountains, levels, fields, coasts and islands.
The Himalayas mountains are isolated into three primary equal ranges—the Great Himalaya or Himadri, Middle Himalaya or Himachal and the Shiwalik.
Toward the south of the Himalayas lie the Northern Indian fields.
In the western piece of India lies the Great Indian desert with little vegetation.
Toward the south of northern fields lies the Peninsular level. It is three-sided fit as a fiddle. This is a locale with various slope extents and valleys. The Aravali slopes, the Vindhyas, the Satpuras are the significant reaches.
The Western Ghats outskirt the level in the west and the Eastern Ghats give the
eastern limit.
Toward the west of the Western Ghats and the East of Eastern Ghats lie the Coastal fields.
Lakshadweep islands are situated in the Arabian ocean while Andaman and Nicobar islands bunch lie toward the south-east of the Indian terrain in the Bay of Bengal.
Landmass: A real estate parcel that is encircled by water on three sides.
Island: A land parcel that is encircled by water on all sides.
Desert: A huge sandy stretch of land.

Alluvial stores: Fine soil brought by streams and saved in the waterway bowls.
Feeder: A little waterway or stream that contributes its water to the fundamental stream by releasing it into the principle stream from either side.
Delta: A region of land framed at the mouth of the stream. It is normally three-sided fit as a fiddle.
Corals: These are skeletons of minuscule marine creatures called polyps.
Tidal wave: A solid and pulverizing harbor wave, created because of a seismic tremor on the ocean bottom.
Waterway: A limited entry of water associating two enormous water bodies like oceans and seas.
(Chapter 7: Our Country India)

