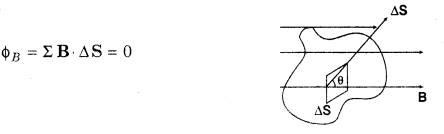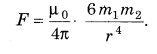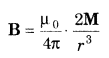Magnetism and Matter:Class 12 Physics NCERT Chapter 5

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 – Magnetism And Matter
In the previous Chapter 4:Moving Charges and Magnetism we have learned about the concepts of Moving Charges and Magnetism.In this Chapter 5:Magnetism And Matter we will learn about the earth’s magnetic field.
Quick revision notes
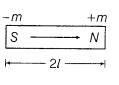
- The magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic dipole is given by
M = m × 2I
where, m is pole strength and 2I is dipole length directed from S to N.
The SI unit of magnetic dipole moment is A-m2 or J/T.
It is a vector quantity and its direction is from South pole to North pole.
- Coulomb’s Law in Magnetism
Magnitude of force acting between two magnetic poles is given by
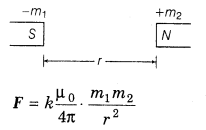
where, m1 and m2 are magnetic strength of poles and k is magnetic force constant. Its SI unit is A-m.
- Magnetic Field Lines These are imaginary lines which give pictorial representation for the magnetic field inside and around the magnet.
Their properties are given as below:
(i) These lines form continuous closed loops.
(ii) The tangent to the field line gives direction of the field at that point.
(iii) Larger the density of the lines, stronger will be the magnetic field.
(iv) These lines do not intersect one another.
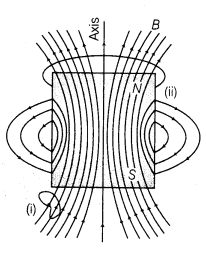
NOTE: The direction of magnetic field between the poles of the dipole is in the direction opposite to the magnetic moment (South to North) while inside the current loop it is in the same direction to that of magnetic moment.
- Torque on a bar magnet in a uniform magnetic field is
![]()
where, θ is the angle between M and B. Its SI unit is joule per tesla (JT-1).
- Potential energy of a magnetic dipole in a magnetic field is given by
U = – MB cos θ = – M . B where, θ is the angle between M and B.
- Work done in rotating the dipole in a uniform magnetic field from θ1 to θ2 is given by
W = MB (cos θ1 – cos θ2)
- Current loop behaves like a magnetic dipole whose dipole moment is given by
M=IA
The direction of dipole moment can be obtained by right hand thumb rule. Its. SI unit is A-m2.
- Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron is given by
![]()
where, v is speed of electron on a circular path of radius r.
L is angular momentum and given as L – mvr.
- Interaction between two magnetic dipoles is

- Oscillation of a Freely Suspended Magnet The oscillations of a freely suspended magnet (magnetic dipole) in a uniform magnetic field are SHM.

where, I = moment of inertia of the magnet, M = magnetic moment and B = magnetic field intensity.
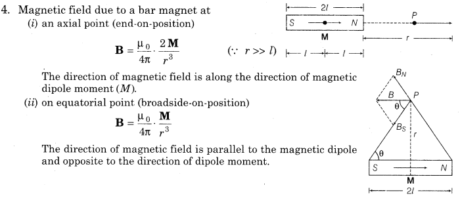
- Bar Magnet as an Equivalent Solenoid The expression of magnetic field at distance r from centre is given by

This expression is equivalent to that of bar magnet.
- The Electrostatic Analog
The table given below summarises the analogy between electric and magnetic dipoles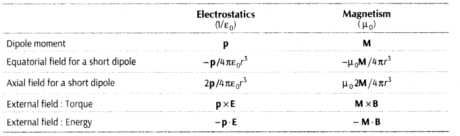
- Magnetism and Gauss’ Law
The net magnetic flux (ФB) through any closed surface is always zero.