Lifelines of National Economy: Class 10 Geography NCERT Chapter 7

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 10 Geography Chapter 7 – Lifelines of National Economy
In the last chapter 6, you learned about Manufacturing Industries. The pace of advancement of a nation depends upon the creation of goods and services and their development over space. Today, the world has been changed over into a considerable town with the assistance of effective and fast-moving transport. Today, India is all around connected with the rest of the world. In this Chapter 7 – Lifelines of National Economic, you will see how current means of transport and communication serve as our country’s lifelines and its cutting edge economy.
Transport
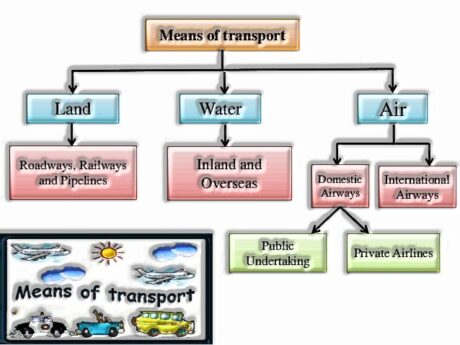
The development of goods and services can be more than three significant domains of our earth, such as land, water, and air. Based on these, transport can also be classified into land, water, and air transport. We should discuss them in detail:
Fast revision notes
-
Roadways :
India has probably one of the largest road networks in the world. Its significance can be seen.
(I) The construction cost of roads is lower than that of railway lines
(ii) Roads can traverse similarly more dissected and undulating geography.
(iii) Roads can arrange higher gradients of slopes and, as such, can cross mountains such as the Himalayas.
(iv) It is prudent in the transportation of barely any persons and moderately smaller measure of goods over short distances.
(v) It provides an entryway to entryway services.
(vi) It is used as a feeder to different modes of transport, such as connecting railway stations, air, and seaports.
Brilliant Quadrilateral Super Highways :
The Govt. had propelled a significant road advancement venture connecting Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi by six-path superhighways.
The North-South corridors are connecting Srinagar [Jammu and Kashmir] &Kanyakumari [T.N.] and East-West Corridor Connecting Silchar (Assam) &Porbander (Gujarat).
The primary goal of these superhighways is to reduce time and distance.
These roadway projects are being actualized by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
Public Highways: National Highways connect extraordinary parts of the nation and are laid and kept up by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
State Highways: State Highways interface a state capital with various district headquarters and are constructed and kept up by the State Public Works Department (PWD) in State and Union Territories.
District Roads: These roads associate the district headquarters with different district places and are kept up by the Zila Parishad.
Other Roads: Rural roads, which interface rural areas and villages with towns. These roads got special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana.
Fringe Roads: Border Roads Organization a Government of India undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the nation’s border areas.
-
Road Density
The length of road per 100 sq. Km of the zone is known as the density of roads.
All roads’ density varies from just 10 km in Jammu and Kashmir to 375 km in Kerala with the public normal of 75 km (1996-97).
III. Railways :
The distribution example of the nation’s railway arrangement has generally been impacting by physiographic, monetary, and administrative factors.
The Himalayan mountains regions are hostile for constructing railway lines because of high alleviation, sparse populace, and every one of monetary opportunities.
The northern plains having high populace density, give an ideal condition to their development
Rivers that require the construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstacles for the construction of railway lines.
IV.Pipelines :
Pipelines transport organize another appearance on the transportation guide of India.
Its underlying cost is high, yet subsequent running costs are negligible.
It is used for transporting unrefined petroleum, oil-based commodities, and flammable gas.
It rules out trans-shipment losses and delays.
Significant Networks
- Oil field in Assam to Kanpur (U.P.), through Guwahati, Barauni& Allahabad.
- From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar. In Punjab through Viramgam, Mathura, Delhi, and Sonipat.
- Gas pipelines from Hazira in Gujarat connect Jagdishpur in UP through Vijaypur in Madhya Pradesh.
- Waterways
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for conveying substantial and bulky goods.

It is an eco-friendly and condition agreeable method of transport.
- Major Sea Ports
With a long coastline of 7,516.6 km, India is spotted with 12 primary and 181 medium and minor ports. Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port that grew soon after Independence.
Kandla is a flowing port. It caters to the advantageous treatment of exports and imports of the exceptionally profitable silo and industrial belt. Mumbai is one of the biggest ports with a spacious characteristic and an all-around sheltered harbor.
Marmagao port (Goa) is the head iron mineral trading port of the country. New Mangalore port, situated in Karnataka, caters to iron metal’s fare concentrates from Kudremukh mines. Kochi is the outrageous south-western port, located at the passage of a tidal pond with a characteristic harbor.
VII. Air Ways:
It can cover exceptionally troublesome terrains like high mountains, inauspicious deserts, dense forests, and long maritime stretches, no sweat.
The air transport was nationalized in 1953.
Air India provides international air services in the whole world.
The renowned Pawan Hans Helicopters Ltd. provides helicopter services to the Oil and Natural Gas Commission in its seaward operations, to inaccessible areas and troublesome terrains like the north-eastern states and the inside parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttaranchal.
(Lifelines of National Economy: Class 10)
VIII. Communication:
Personal communication and mass communication, including television, radio, press, films, and so on, are the primary means of communication.
The Indian postal system is by far the largest in the world. Cards and envelopes are considered first-class mail.
The second–class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers, and periodicals.
To encourage mails’ speedy conveyance in enormous towns and cities, six mail channels have been presented as of late.
They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel, and Periodical Channel. With the transportation and postal services being the biggest, India also has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia.
- International Trade :
The trading of goods among individuals, states, and countries is referred to as a trade. The exchange of goods/ trading between the two countries is called International Trade.
Exports and imports are the components of the trade. The equalization of an exchange of a nation is the contrast between its fare and import.
At the point when the estimation of exports exceeds the assessment of imports, it is called the positive parity of trades.
- Tourism as a Trade :
Tourism has substantiated itself as one of the most significant aspects of the trade.
Tourism in India has developed substantially.
It helps as an advancement of National Integration.
Offer help to neighborhood handicrafts.
Provides support to social pursuits.
Improvement of international understanding about our way of life and legacy.
(Lifelines of National Economy: Class 10)

