Inside Our Earth: Geography Class 7 Chapter-2

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 – Inside Our Earth
Quick revision notes
In Chapter 1 of Class 8 NCERT book: you must have learnt about Environment on Earth In chapter 2: you will learn about inside of the Earth.
Planet Earth
- The earth in which humans live is not absolute spherical in shape.
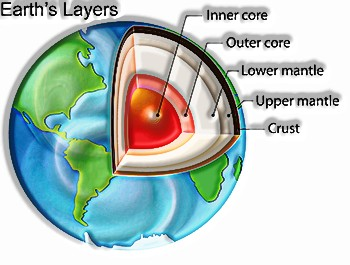
Interior of earth
- The earth is like onion which is made up of several layers.
Crust
- The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface is called the crust.
- It is the thinnest of all the layers.
→ It is 35 km thick on the landmass (continental masses) and only 5 km on the ocean floors.
- Main mineral constituents of the continental mass: Silica and Alumina.
→ Thus, it is called sial (si-silica and al-alumina).
- The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium
→ Thus, it is called sima (si-silica and ma-magnesium).
Mantle
• This layer extends up to a depth of 2900 km below the crust.
Core
• The innermost layer is the core.
- The radius of core is about 3500 km.• It is mainly made up of nickel and iron.
→Thus, it is called NiFe (Ni – nickel and Fe – ferrous i.e. iron).• The central core has very high temperature and pressure.
What is Earth?
- The earth includes three layers: outside, mantle and center.
- Steady changes happen inside just as outside the earth.
What is the Interior of the Earth?
- The earth is comprised of three concentric layers-hull, mantle and center.
- The highest layer over the world’s surface is known as the hull. It is around 35 km thick on the mainland masses and just 5 km thick on the sea floor. It is comprised of silica and alumina and in this manner called sial.
- The maritime outside layer primarily comprises of silica and magnesium called sima. Just beneath the outside is the mantle up to a degree of 2,900 km.
- The deepest layer is the center with a sweep of 3,500 km. As it is made of nickel and iron, it is called nife(ni-nickel and fe-ferrous for example iron). The focal center has a high temperature and weight.
Rocks and Minerals
- The world’s outside layer is made of different sorts of rocks. Any normal mass of mineral issue that makes up the world’s hull is known as a stone.
- There are three significant kinds of rocks; molten rocks, sedimentary rocks and transformative rocks.
- At the point when the liquid magma cools, it gets strong. Shakes in this manner framed are called molten or essential rocks. They are of two kinds, extrusive volcanic rocks and meddlesome molten rocks.
- Rocks fold down and break into little sections and these littler particles are called silt. These silt are moved, packed and solidified to shape layers of rocks. These kinds of rocks are called sedimentary stone.
- Molten and sedimentary rocks can change into transformative rocks under incredible warmth and weight. The cycle of change of the stone starting with one then onto the next is known as the stone cycle.
- Rocks are made of various minerals. Minerals are normally happening substances which have certain physical properties and clear concoction organization.
The earth is continually going through changes inside and outside. Hence, it is known as a powerful planet.
The earth is comprised of a few concentric layers. The highest layer over the earth is the surface is known as the covering. It is the most slender of the apparent multitude of layers.
The mantle is simply underneath the covering.
The deepest layer is the center with a range of around 3500 km.
The focal center has an extremely high temperature and weight.
The world’s covering is comprised of a few kinds of rocks.
There are three sorts of rocks—volcanic rocks, sedimentary rocks and transformative rocks.
Molten rocks are additionally called essential rocks. They are of two kinds—meddlesome rocks and extrusive rocks.
Extrusive molten rocks have an exceptionally fine-grained structure. For instance, basalt.
Nosy volcanic rocks are framed somewhere inside the earth. Stone is a case of this stone.
Sedimentary rocks are framed by the residue, which are little pieces of rocks. For instance, sandstone is produced using grains of sand.
Volcanic and sedimentary rocks can change into transformative rocks under incredible warmth and weight. For instance, mud changes into record and limestone into marble.
Hard shakes are utilized for making streets, houses and structures.
One sort of rock changes to another kind under specific conditions in a cyclic way. This cycle of change of the stone starting with one then onto the next is known as the stone cycle.
Rocks are comprised of different minerals.
Minerals are normally happening substances which have certain physical properties and unequivocal compound sythesis. Minerals are fundamental for individuals.
Outside or Crust: The highest layer over the world’s surface. It is slender.
Soal: The mainland mass of the covering comprising of silica and alumina is called sial (si-silica and al-alumina).
Sima: The maritime outside layer for the most part comprises of silica and magnesium. It is accordingly called sima (si-silica and mama magnesium).
Mantle: This layer is simply underneath the hull. It reaches out up to a profundity of 2900 km. underneath the hull.
Rock: A stone is a characteristic mass of mineral issue that makes up the world’s outside.
Volcanic stone: These stones are shaped by cooling and cementing liquid magma.
Magma: It is searing red liquid magma coming out from the inside of the earth on its surface.
Extrusive volcanic stone: When the liquid magma goes ahead the world’s surface, it quickly chills off and gets strong. Rocks shaped thusly on the covering are called extrusive molten rocks.
Meddlesome volcanic stone: When the liquid magma chills off somewhere inside the world’s outside layer strong nosy molten rocks are shaped.
Silt: These are little parts of rocks.
Sedimentary stone: When free silt are packed and solidified, layers of rocks are shaped. These sorts of rocks are known as sedimentary rocks.
Rock cycle: The cycle of change of the stone starting with one then onto the next is known as the stone cycle.
Mineral: Minerals are normally happening substances which have certain physical properties and unequivocal synthetic structure.

