Globalisation And The Indian Economy: Class 10 Economics NCERT Chapter 4

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 – Globalisation And The Indian Economy
In the last chapter 3: Money And Credit, you learned about money and credit and its uses. In this Chapter: Globalisation And The Indian Economy, you will learn about Globalization and the Indian Economy, we have fundamentally managed the Integration of production and combination of markets. This will assist you with understanding the process of globalization and its impact in a superior manner.

This section deals with globalization. Here you will become acquainted with the coordination between countries through unfamiliar exchange and unfamiliar investments by multinational corporations (MNCs). You will additionally become more acquainted with the job that MNCs plays in the globalization process. The last section of the part covers the impact of globalization and the degree to which globalization added to the advancement process.
(Globalisation And The Indian Economy: Class 10)
Production Across Countries
Exchange was the fundamental channel associating distant countries. Enormous companies which are presently called Multinational Corporations (MNCs) assume a significant job in exchange. A MNC is an organization that owns or controls production in more than one country. MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get modest work and different resources so that the organization can gain more prominent profits.
(Globalisation And The Indian Economy: Class 10)
Speedy revision notes
PRODUCTION ACROSS COUNTRIES:
- Until the center of the twentieth century, production was to a great extent sorted out inside countries.
- Colonies such as India send out the crude materials and food stuff and imported finished goods.
- Exchange was the primary channel associating distant countries. This was done before huge companies called multinational partnership (MNCs) rose on the scene.
- A MNC is an organization that owns or controls production in more than one country.
- MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get modest work and different resources.
- MNCs are selling its finished products universally as well as more significantly, the goods and services are created all inclusive.
- As a result, production is composed in increasingly complex ways.
INTERLINKING PRODUCTION ACROSS COUNTRIES:
- As a rule, MNCs set up production where it is close to the markets; where there is skilled and unskilled work accessible at low costs; and where the accessibility of different factories of production is assured.
- The cash that is spent to purchase assets such as land, building, machines and other gear is called investment. The investment made by the MNCs is called unfamiliar investment.
- The advantage to the nearby organization of such joint production is two-overlay.
(I) MNCs can give cash to extra investments, such as purchasing new machines for faster production.
(ii) MNCs may carry with them the latest technology for production.
- Yet, the most widely recognized course for MNC investments is to purchase up nearby companies and afterward to extend production.
- Huge numbers of the top MNCs have riches surpassing the whole financial plan of the creating nation government.
- We see that there are an assortment of ways where the MNCs are spreading their production and interacting with neighborhood producers in various countries across the globe.
- MNCs are applying a strong effect on production at these distant locations.
- As a result, production in these broadly dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
FOREIGN TRADE AND INTEGRATION OF MARKETS:
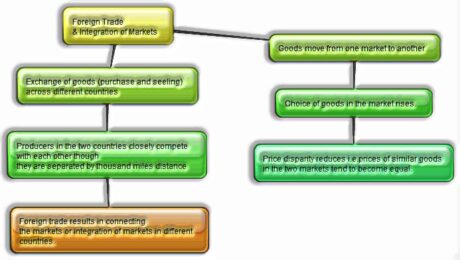
- Unfamiliar exchange creates an open door for the producers to reach past the domestic markets i.e., markets of their own countries.
- For the buyers, import of goods delivered in another nation is one method of growing the selection of goods past what is domestically created.
- By and large, with the launch of exchange, goods go starting with one market then onto the next.
- Unfamiliar exchange thus results in associating the markets or incorporation of markets in various countries.
WHAT IS Globalization?
- A huge portion of the unfamiliar exchange is also constrained by MNCs.
- A result of more noteworthy unfamiliar exchange has been more prominent unfamiliar exchange has been more prominent reconciliation of production and markets across countries.
- Globalization is this process of fast incorporation or interconnection between countries.
- MNCs are assuming a significant job in the globalization process.
- An ever increasing number of goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries.
FACTORIES THAT HAVE ENABLED Globalization:
- Quick improvement in technology has been on a central point that has stimulated the globalization process.
- For instance, the past 50 years have seen several improvements in transportation technology.
- Considerably more striking have been the advancement of data and correspondence technology.
- Technologies in the areas of telecommunications, computers, and web have been evolving quickly.
Advancement of unfamiliar exchange and unfamiliar investment strategy:
- Expense on imports is a case of exchange obstruction. It is known as an obstruction because some restriction has been set up.
- The administration can use exchange barriers to increase or decrease unfamiliar exchange and to choose what sort of goods and the amount of each, should come into the nation.
- The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to unfamiliar investment.
- This was considered necessary to shield the producers inside the nation from unfamiliar rivalry.
- Barriers to unfamiliar exchange and unfamiliar investment were eliminated to an enormous degree.
- This implied goods could be imported and sent out easily and furthermore unfamiliar companies could set up factories and offices here.
- Eliminating barriers or restrictions set by the administration is what is known as advancement.
- The legislature imposes substantially less restriction than previously and is consequently said to be more liberal.
WORLD TRADE Organization:

- We have seen that the advancement of unfamiliar exchange and investment in India was supported by some incredible international association.
- These organizations say that all barriers to unfamiliar exchange and investment are destructive. There should be no barriers.
- World Trade Organization (WTO) is one such association whose point is to change international exchange.
- Despite the fact that WTO is supposed to permit international commerce for all, in practice, it is seen that the created countries have unreasonably held exchange barriers.
- Then again, WTO rules have constrained the creating countries to eliminate the exchange barriers.
IMPACT OF Globalization IN INDIA:
- In the last twenty years, globalization of the Indian economy has made some amazing progress.
- Globalization and more prominent rivalry among producers – both nearby and unfamiliar producers – has been of preferred position to consumers, especially the wealthy sections in the urban areas.
- As a result, these individuals today appreciate a lot better expectations of living than was possible before.
- MNCs have increased their investments in India in the course of recent years, which means investing in India has been valuable for them.
- Several of the top Indian companies have had the option to profit by the increased rivalry.
- Also, globalization has empowered some enormous Indian companies to rise as multinationals themselves!
- Globalization has also made new opportunities for companies offering types of assistance, especially those including IT.
THE STRUGGLE FOR A FAIR Globalization:
- Individuals with training skills and riches have utilized new opportunities.
- Then again, there are numerous individuals who have not shared the benefits.
- Reasonable globalization would make opportunities for all and furthermore ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared better.
- The legislature can assume a significant job in making this possible.
- Its policies must secure the interests of the rich and the amazing as well as all the individuals in the nation.
- It can support small producers to improve their presentation till the time they become strong enough to contend.
- On the off chance that necessary, the legislature can use exchange and barriers.
- In the past hardly any years, massive campaigns and representatives by individuals’ organizations have affected significant decisions identifying with exchange and investments at the WTO.
- This has demonstrated that individuals also can assume a significant job in the struggle for reasonable globalization.

