Forests Our Lifeline: Class 7 Science NCERT Chapter 17

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 7 Science Chapter 17 – Forests: Our Lifeline
In the last chapter 16, you learned Water. In this chapter, you will be learning about Forests and how it actually works in our life.
Quick revision notes
In ancient occasions, we used to live in forests. It met all our necessities for leading a normal life around then. Now-a-days, we live in urban areas and towns far off from forests, so we really don’t know the importance of forests throughout our life. It is a natural renewable asset a habitat (home) to many types of untamed life like bear, buffalo, jackal, deer, porcupine, elephant, and so forth.
Many trees like sal, teak, semal, Sheesham, neem, Palash, fig, khair, amla, bamboo, kachnar and many others are also found in the forests. The forest also contains bugs, butterflies, bumble bees and winged creatures which help in palliation in the blossoming plants of the forest in pollination.
Structure of a Forest
The plants (trees, bushes and herbs) make various layers in the forest which are depicted beneath:
- Canopy
The highest branches and leaves of tall trees which act as a rooftop over the forest ground is called canopy. It is the most elevated layer of vegetation in the forest. The branch part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.
- Understorey
The distinctive horizontal layers shaped because of various kinds of crowns in the forest is called understorey. The constituents of understorey can be portrayed as follows:

(I) Top layer It comprises the gaint and tall trees followed by bushes and tall grasses.
(ii) Shrub layer It has many bushes and brambles of approximately 1-2 meters of range from the forest floor. It makes thick layer at certain places of forest where enough daylight is available.
(iii) Herb layer Just underneath the bush layer happens the herb layer of plants. It is the most reduced layer of vegetation in the forest (having leafy plants). The greater part of the plants in herb layer have short lifespan.
(iv) Forest floor Plants discovered here are as small as mosses, liverworts, lichens. It has many sorts of creepy crawlies, worms, toad stool, and so on. A large portion of the forest floor is secured with dead and decaying plant matter, and animal waste.
Segments of the Forest
The living organisms found in the forest are plants, animals, decomposers and scavengers. The non-living condition of the forest gives supplements, water and carbon dioxide for the development of the plants.
- Plants
Green plants are living organisms also called autotrophs as they produce food by photosynthesis (by absorbing supplements water from soil, CO2 from air and daylight as vitality source). They give food to all living organisms which live in the forest. They are called makers (of food).
- Animals
Forests have many animals and they are called consumers (of food). The animals which eat just plants/their parts are called herbivores (herb eating) whereas flesh-eating animals are called carnivores. All animals are called heterotrophs because they rely upon different organisms for food.
- Decomposers
Generally these organisms are microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. They feed on dead plants and animals and hence are called saprotrophs. These organisms are also called decomposers as they breakdown dead parts of plants and dead groups of animals into simple substances. They play an important job in sustaining the forests.
- Scavengers
Those animals which eat dead animals are called scavengers, for example vultures, crows, jackals, hyena, a few creepy crawlies (ants, insects, termites, woodlice, maggots, millipedes and earthworms), and so forth. Scavengers are the cleaning agents of our condition. However, these are not decomposers as they don’t breakdown complex dead organic matter into simple ones.
Importance of Forests
The forests give us countless items. They also clean air and water quality and maintain soil dampness and climate. Along these lines, they are called help.
- Forests Provide Many Useful Products
The various things which are obtained from the forests are called forest items. Forests give us countless helpful items. A portion of the important items which we get from the forests are wood, nectar, gum, sealing wax (or lac), catechu (kattha), fruits, oils, spices, natural rubber, cork, dyes, medicinal plants and fodder for cattle. Perhaps the most important item obtained from forests is the wood (which is obtained by chopping down the forest trees). The wood obtained from forests is utilized for countless purposes in our day-to-day life.
- Forests Maintain Balance among Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Plants in the forest release oxygen during photosynthesis. This furnishes all animals incorporating us with oxygen to breathe and assists with maintaining the ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That is the reason, forests are called green lungs.
On the off chance that the amount of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, it would bring about an increase in earth’s temperature. Plants in the forest intake carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. Subsequently, they help to maintain the perfect amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Forests Maintain Water Cycle
The forest trees suck water from the dirt through their underlying foundations and release water vapor into the air through transpiration. This water vapor helps in the formation of mists and welcome rain on the earth. Along these lines, forests welcome adequate rainfall on the earth. In fact, about half the rain which falls in forest areas originates from the transpiration of forest trees themselves. Along these lines, forests help in maintaining an ideal water cycle in nature and meet our freshwater prerequisites.

- Forests Prevent Occurrence of Flood
The forest goes about as a characteristic safeguard of water and permits it to leak. It assists with keeping up the water table consistently. Forests help in controlling floods as well as help to keep up the progression of water in the streams with the goal that we get a consistent flow of water.
Then again, if trees are absent, downpour hits the ground directly and may flood the region around it. Substantial downpour may likewise harm the soil. Foundations of trees typically bind the soil together, however in their nonappearance, the soil is washed away or dissolved.
The various types of plants become together in the forest creating various degrees of layers and living space for wild creatures. Without plants/trees, the soil won’t stand up to anything which will cause flood and disintegration.
- Forests Provide Habitat for Wildlife
The various kinds of vegetation present in a forest give food and haven to creatures, winged animals and creepy crawlies which live in the forest. This makes a food chain.
Food chain
Food chain can be characterized as a grouping of living creatures wherein one life form benefits from another.
An average chain in grassland is: grass → deer → lion
An average food chain in a lake is: algae → small fish → big fish
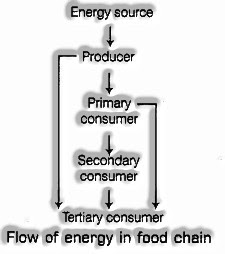
Stream of Energy in a Food Chain
The sun is a definitive source of energy for everything on the planet. Green plants or producers can tackle the energy of the sun to make food. In a food Flow energy in food chain, energy from plants (producers) is given starting with one creature then onto the next. From the producers, the energy goes to essential shoppers (herbivores) and is then given to auxiliary purchasers (carnivores). Along these lines, producers are consistently toward the start of the food chain.
Dynamic Living Entity
By holding more prominent assortment of plants, the forest gives incredible chances of food and natural surroundings for the herbivores. Bigger number of herbivores implies expanded accessibility of food for an assortment of carnivores. The wide assortment of creatures causes the forest to recover and develop. Decomposers help in keeping up the flexibly of supplements to the developing plants in the forest. Consequently, the forest is a unique living substance. There is a persistent connection between soil, water, air, plants and creatures in a forest.
- Forests can Regenerate all alone
The dead pieces of trees and plants, dead creatures and creature squanders (like creature excrement or droppings) continue gathering on the forest floor. Decomposers (parasites and microbes) corrupt them into basic natural substances which are usable by plants as humus. The hummus makes the forest soil prolific by giving the supplements. The creatures, fowls of forests, wind and water scatter the seeds of trees and plants on the forest soil. These seeds acquire supplements from the soil and develop to frame seedlings and eventually develop to shape the forest vegetation.
Forest Conservation
Paper is produced using wood mash that is created from the wood of forest trees. Thus, to make paper, numerous trees must be chopped down from the forests. In the event that we all continue gathering old papers, magazines, books, journals, and so on., and send them to paper plants for reusing through a garbage vendor (kabadi wala), we will have the option to spare many forest trees from being chopped down.
A portion of different approaches to conserve forests are likewise given underneath:
- Unreasonable chopping down of forest trees ought not be permitted by the administration to conserve forests.
- More trees ought to be planted in the forest instead of chop down trees to conserve forests.
- Paper items, for example, old papers, magazines, books, journals, and so on., ought to be reused to conserve forests.
Countless forest trees are being chopped during each time to satisfy the different needs of the expanding populace. This is called deforestation. Following are the result if forests vanish:
- Increment of the world’s temperature If there are no trees and plants, their will be no photosynthesis. Along these lines, no C02 of the air will be utilized. This will expand the degree of C02, bringing about the expansion of earth’s temperature.
- No food and sanctuary to untamed life without trees, plants and creatures won’t get food and safe house. Along these lines, this will upset the entire pattern of life and bit by bit life may vanish from the land territory of the earth.
- There will be more floods The trees plant establishes help in holding the soil during downpours and furthermore soil can hold water. Without trees, the soil won’t stand any kind of test which will cause floods.
- Deforestation imperil the condition The persistent deforestation is undermining the diverse type of life including people. Along these lines, there is need to think and set to conserve forests. Regular cataclysms like floods, typhoons, hail structures are more without trees and forest. Individuals become homeless when such catastrophe happens.

