Environmental Chemistry: Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Chapter 14

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Environmental Chemistry
In the last chapter 13, you learned about Hydrocarbons. In this chapter: Environmental Chemistry, you will learn about Pollution. Pollution is a term that is recognizable to everyone nowadays… It has become so regular that nearly everybody is thinking about how Pollution is rising consistently every day. The term ‘pollution’ alludes to the indication of any bothersome unfamiliar undesirable substance in something. When we state Pollution on earth, we allude to the tainting that is going on around natural assets by different pollutants. This is fundamentally brought about by human exercises, which hurt the earth in one way or another. Hence, a pressing need has emerged to handle this issue straight away and dispose of it. Subsequently, Pollution is harming our earth harshly, and we have to understand its belongings and forestall this harm before it’s past the point of no return.
(Environmental Chemistry: Class 11)
Quick Revision notes
- Air, Water and Soil Pollution
- Chemical Reactions in Atmosphere-smog, acid rain
- Ozone and Its Reactions, Greenhouse impacts and Global warming
- Techniques to control Environmental Pollution
Environmental chemistry assumes a noteworthy job in nature. Chemical species present on the earth are either frequently happening or created by human exercises.
Environmental Pollution is the impact of unwanted changes in ecological factors that effectively affect plants, creatures, and individuals.
Toxin: – A substance, which causes Pollution, is known as contamination.
Pollutants can be stable, liquid, or gaseous substances present in more noteworthy fixation than in nature and are delivered because of human exercises or because of characteristic happenings.
For instance, substances such as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), plastic materials, overwhelming metals, numerous chemicals, nuclear squander, and so on, once delivered into the earth are hard to expel.
Pollutants can be Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable:-
Biodegradable pollutants: These are the pollutants that are quickly separated by characteristic procedures. Model: disposed of vegetables
Non – biodegradable pollutants: These are the gradually degradable pollutants, and stay in the earth in an unaltered structure for a long time.
Environmental Pollution is of three sorts:
- Atmospheric Pollution
- Tropospheric Pollution
- Stratospheric Pollution
Atmospheric Pollution is commonly concentrated as tropospheric and stratospheric pollution.
Atmospheric Pollution happens when the centralization of an ordinary segment of the air or another chemical substance included or framed in the air develops to unwanted proportions making hurt people, different creatures, vegetation, and materials.
The most minimal locale of atmosphere wherein the individuals, alongside different creatures live, is known as the troposphere. It reaches out up to the tallness of ~ 10 km from the ocean level. The troposphere is a violent, dusty zone containing air, much water fume, and mists.
Tropospheric Pollution:- The explanation behind the occurrence of Tropospheric Pollution is the nearness of undesirable strong or gaseous particles present in the atmosphere.
The accompanying underneath is the major gaseous and particulate pollutants found in the troposphere:
Gaseous air pollutants are primarily oxides of sulfur, nitrogen and carbon, hydrogen sulfide, hydrocarbons, ozone, and different oxidants.
Particulate pollutants: These are dust, fog, vapor, smoke, smog, and so on.
Acid rain: Normally, rainwater has a pH of 5.6 because of the nearness of H+ ions framed by rainwater reaction with carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere.
+ CO2(g) — > H2CO3(aq)
Source: Burning petroleum derivatives (which contain sulfur and nitrogenous matter, for example, coal and oil in power stations and heaters or petroleum and diesel in engine motors produces sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide.
SO2 and NO2 after oxidation and reaction with water are significant supporters of acid rain because contaminated air, for the most part, contains particulate matter that catalyzes the oxidation.
(Environmental Chemistry: Class 11)
Harmful impacts:-
Unsafe for farming, trees, and plants break down and squander the supplements required for their development.
Causes respiratory afflictions in individuals and creatures.
Influences plant and creature life in the oceanic environment when acid rain falls and streams as groundwater arrives at waterways, lakes, and so on. Erodes water pipes bring about the draining of overwhelming metals, such as iron, lead, and copper, into the drinking water.
Harms structures and different structures are made of stone or metal. The Taj Mahal in India has been influenced by acid rain.
The gaseous pollutants come down to the earth as acid rain.
Greenhouse impact: Nearly 75 % of the sun based vitality that arrives at the earth is consumed by the world’s surface, which builds its temperature. The remainder of the warmth emanates back to the atmosphere. A portion of the heat is caught by gases, for example, carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbon mixes (CFCs), and water fume in the atmosphere. In this way, they add to the warming of the atmosphere. This causes global warming.
This catching of the sun’s warmth close to the world’s surface and keeping it warm is known as the regular greenhouse impact. It keeps up the temperature and makes the earth ideal forever.
The world’s surface ingests 75% of the sunlight based vitality arriving at the earth, and rest is transmitted back to the atmosphere. These gases referenced above snare the warmth, which brings about global warming.
It is basic to understand that these very gases are additionally liable for life on the earth as they trap some measure of sunlight based vitality for the food of life. The expansion in these greenhouse gases is raising the temperature of the world’s atmosphere, which, if not checked, may, in the long run, bring about the dissolving of polar ice tops, and this way may lower the beachfront landmass.
Smog: Smog is a blend of smoke, dust particles, and little drops of haze.
Classical Smog Photochemical Smog
It happens in a chilly, muggy climate. It occurs in a warm, dry, and bright climate.
It is a blend of smoke, mist, and sulfur dioxide. Components of photochemical
result from daylight unsaturated hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxide
created via vehicles and processing plants.
It is likewise called lessening smog. It is additionally called oxidizing smog.
Stratosphere: Above the troposphere, somewhere in the range of 10 and 50 km above ocean level lies the stratosphere. The ozone layer is the primary constituents of the stratosphere. The nearness of ozone in the stratosphere forestalls about 99.5 percent of the sun’s harmful bright (UV) radiation from arriving at the world’s surface, in this way shielding people and different creatures from its impact.
Arrangement and Breakdown of Ozone
The upper stratosphere comprises a lot of ozone (O3), which shields us from the hurtful bright (UV) radiations (255 nm) originating from the sun. The UV radiations split separated sub-atomic oxygen into free oxygen (O) molecules. These oxygen iotas join with the atomic oxygen to shape ozone.
O2 (g) — UV–→ O (g) + O (g)
O (g) + O2 (g) ⇋ O3 (g)
Ozone is thermodynamically insecure and decays to sub-atomic oxygen. In this way, a unique harmony exists between the creation and decay of ozone particles.
Numerous human exercises are creating chemicals responsible for the consumption of the ozone layer in the stratosphere, prompting the arrangement of the ozone opening.
Consumption of the ozone layer
The primary purpose behind ozone layer exhaustion is accepted to be the arrival of chlorofluorocarbon mixes (CFCs), otherwise called freons.
These mixes are utilized in coolers, air conditioners, the creation of plastic froth, and the electronic business for cleaning PC parts.
When CFCs are delivered in the atmosphere, they blend in with the ordinary atmospheric gases and inevitably arrive at the stratosphere. In the stratosphere, they get separated by amazing UV radiations, delivering chlorine-free radicals.
— – UV— — > Cl. (g) +CF2Cl. (g)
(g) + O3 (g)— — > ClO.(g) + O2(g)
ClO.(g) + O(g)— — – > Cl.(g)+ O2 (g)
Along these lines, the chlorine radicals are constantly recovered and cause the breakdown of the ozone layer. Subsequently, CFCs are shipping specialists for reliably creating chlorine radicals into the stratosphere and harming the ozone layer.
Impacts of Depletion of the Ozone Layer
UV radiations lead to maturing of the skin, waterfall, burn from the sun, malignant skin growth, the murdering of numerous phytoplanktons, harm to fish profitability, and so on.
Likewise, it has been accounted for that plant proteins are effectively influenced by UV radiation, prompting the destructive transformation of cells.
It likewise expands the dissipation of surface water through the leaves’ stomata and diminishes the dampness substance of the soil.
An expansion in UV radiation harm paints and strands, making them blur quicker.
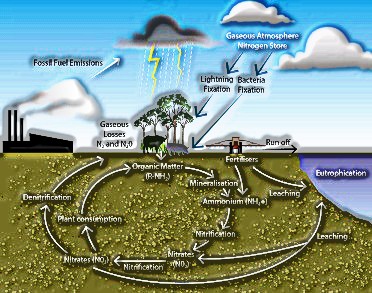
Water is the remedy of life, yet similar water, whenever dirtied by microbes, natural squanders, overwhelming harmful metals, pesticides, and so on., will transform into poison.
(Environmental Chemistry: Class 11)
WATER POLLUTION
Water is necessary forever. Pollution of water starts from human exercises. In various ways, Pollution arrives at the surface or groundwater. Effectively recognized source or a spot of
Pollution is known as a point source. e.g., civil and modern release pipes where pollutants enter the water-source.
Nonpoint wellsprings of Pollution are those where a wellspring of Pollution can’t be handily distinguished, e.g., agrarian spillover (from the ranch, animals, and yield lands), acid rain, storm-water drainage (from avenues, parking garages, and gardens), and so on.
Reasons for Water Pollution
Microorganisms: The most severe water pollutants are the infection causing operators called microbes. Microbes incorporate organisms and different creatures that enter the water from household sewage and creature excreta. Human excreta contain bacteria, for example, Escherichia coli and Streptococcus faecalis, which cause gastrointestinal illnesses.
Natural squanders: The other significant water contamination is a natural matter, for example, leaves, grass, rubbish, etc.
Significant Water Pollutants
Pollutant Source
Small scale organisms Domestic sewage
Natural wastes Domestic wastewater, creature excreta,
rotting creatures and plants, release from industrial food facilities
Plant nutrients Chemical manures
Poisonous overwhelming metals Industries and chemical processing plants
Sediments Erosion of soil by agribusiness and strip mining
Pesticides Chemicals utilized for slaughtering bugs, parasites, and weeds
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD): The measure of oxygen required by microscopic organisms to separate the natural matter present in a particular volume of a water test is called BOD.
Eutrophication: The procedure where supplement advanced water bodies bolster a thick plant populace, which murders creature life by denying it of oxygen and results in ensuing loss of biodiversity, is known as eutrophication.
Worldwide Standards for Drinking Water
Fluoride: For drinking purposes, water ought to be tried for fluoride particle focus. Its lack of drinking water is unsafe to man and causes illnesses, such as tooth rot and so forth. Dissolvable fluoride is frequently added to drinking water to bring its fixation upto one ppm.
Or, on the other hand, 1 mg dm–3.
Lead: Drinking water gets tainted with lead when lead pipes are utilized for the transportation of water. The recommended furthest breaking point centralization of lead in drinking water is around 50 ppb. Lead can harm the kidney, liver, regenerative framework, and so forth.
Sulphate: Excessive sulfate (>500 ppm) in drinking water causes the diuretic impact, in any case
At moderate levels, it is innocuous.
Nitrate: The highest furthest reaches of nitrate in drinking water is 50 ppm. Overabundance nitrate in drinking water can cause infection, such as methemoglobinemia (‘blue child’ disorder).
Different metals: The enormous centralization of some healthy minerals suggested in
Drinking water.
Fe 0.2 ppm
Al 0.05 ppm
Mn 0.2 ppm
Cu 3.0 ppm
Zn 5.0 ppm
Cd 0.005 ppm
This way, one should take care to observe worldwide guidelines to keep up virtue levels of drinking water. Modern squanders, and unreasonable utilization of pesticides bring about Pollution of landmass and water bodies.
Techniques for controlling environmental Pollution can be:
Squander the board, i.e., a decrease of the waste and appropriate removal, likewise reusing of materials and vitality,
Squander the board
Separate the loss as biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste:
Biodegradable waste: Generated by cotton factories, food preparing units, paper
Plants and material production lines.
The boards are kept in landfills and are changed over into manure.
Non – biodegradable waste: Generated by warm force plants that produce fly debris; coordinated iron and steel plants which produce impact heater slag and steel dissolving slag.
The executives:
– Recycling
– Toxic squanders are generally annihilated by controlled burning
Green chemistry: Green chemistry is a methodology to plan chemical procedures and items that decrease or dispense with the utilization and age of dangerous substances. The chemical reactions ought to be with the end goal that the reactants are wholly changed over into essential, environmentally benevolent items. They utilize a well-disposed domain medium so that there would be no toxin in nature around.
Green chemistry in regular daily existence:
The material is laundered with the utilization of hydrogen peroxide to supplant chlorine.
Paper Bleaching is presently finished with hydrogen peroxide.
Union of chemicals like ethanal is finished with a stage oxidation process.
(Environmental Chemistry: Class 11)
Questions
Q.1 What are the outcomes of Pollution?
A.1 Pollution chiefly influences the nature of human and sea-going life. It debases everything from the water we drink to the air we relax. It devastates the common assets required for a sound and long life.
(Environmental Chemistry: Class 11)

