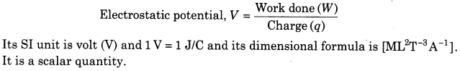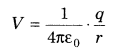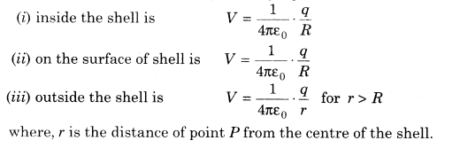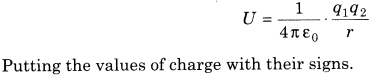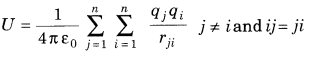Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance:Class 12 Physics NCERT Chapter 2

Key Features of NCERT Material for Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 – Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In the previous Chapter 1: Electric charges and fields we have learned about forces between two charged particles and their properties.In this Chapter 2:Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance we will learn potential energy of the system of charges.
Quick revision notes
- Electrostatic Potential The electrostatic potential anytime in an electric field is equivalent to the measure of work done per unit positive test charge or in bringing the unit positive test charge from endless to that point, against the electrostatic power without quickening.

NOTE: Electrostatic potential is a state subordinate capacity as electrostatic powers are moderate powers.
- Electrostatic Potential Difference The electrostatic likely distinction between two focuses in an electric field is characterized as the measure of work done in moving a unit positive test charge from one highlight the other point against of electrostatic power with no quickening (for example the distinction of electrostatic possibilities of the two focuses in the electric field).
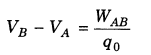
![]()
where, is work done in assuming responsibility q0 from A to B against of electrostatic power.
Likewise, the line vital of electric field from beginning position A to definite position B along any way is named as expected distinction between two focuses in an electric field, for example
NOTE: As, work done on a test charge by the electrostatic field because of some random charge design is free of the way, henceforth potential distinction is additionally same for any way.
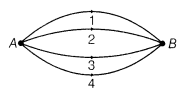
For the chart given as beneath, expected contrast between focuses An and B will be same for any way.
- Electrostatic potential because of a point charge q anytime P lying a good ways off r from it is given by

- The potential at a point due to a positive charge is positive while due to negative charge, it is negative.
- At the point when a positive charge is put in an electric field, it encounters a power which drives it from purposes of higher potential to the purposes of lower potential. Then again, a negative charge encounters a power driving it from lower potential to higher.
- Electrostatic potential because of an electric dipole anytime P whose position vector is r w.r.t. mid-purpose of dipole is given by

- The electrostatic potential on the opposite bisector because of an electric dipole is zero.
- Electrostatic potential anytime P because of an arrangement of n point charges q1, q2, … , qn whose position vectors are r1,r2,… ,rn individually, is given by
where, r is the position vector of point P w.r.t. the cause.
.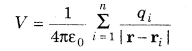
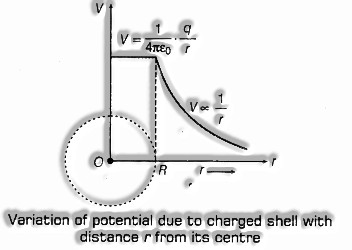
- Electrostatic potential because of a slender charged circular shell conveying charge q and range R individually, anytime P lying

- Graphical representation of variety of electric potential because of a charged shell a ways off r from focus of shell is given as underneath:

11 Equipotential Surface of variety of electric potential because of a charged shell a ways off r from focus of shell is given as underneath:
A surface which have same electrostatic potential at each point on it, is known as equipotential surface.
The state of equipotential surface due to
(I) line charge is barrel shaped.
(ii) point charge is circular as appeared close by:
(an) Equipotential surfaces don’t cross each other as it gives two bearings of electric field E at converging point which is unimaginable.
(b) Equipotential surfaces are firmly divided in the area of solid electric field and the other way around.
(c) Electric field is consistently ordinary to equipotential surface at each purpose of it and coordinated from one equipotential surface at higher potential to the equipotential surface at lower potential.
(d) Work done in moving a test charge from one purpose of equipotential surface to other is zero. 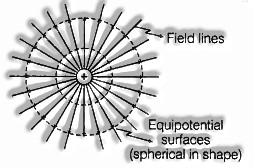
- Connection between electric field and likely slope
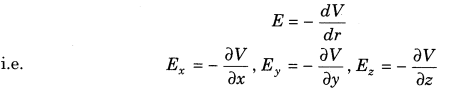
where, negative sign demonstrates that the bearing of electric field is from higher potential to bring down potential, for example toward diminishing potential.
NOTE: (I) Electric field is toward which the potential reductions steepest.
(ii) Its greatness is given by the adjustment in the extent of potential per unit dislodging typical to the equipotential surface at the point.
- Electrostatic Potential Energy The work done against electrostatic power gets put away as likely vitality. This is called electrostatic likely vitality.
∆U = UB-UA =WAB
- The work done in moving a unit positive test charge over a shut way in an electric field is zero. Hence, electrostatic powers are traditionalist in nature.
- Electrostatic expected vitality of an arrangement of two point charges is given by

- Electrostatic potential of a system of n point charges is given by

- Potential Energy in an External Field
(I) Potential Energy of a solitary charge in outer field Potential vitality of a solitary charge q at a point with position vector r, in an outside field is qV(r),
where V(r) is the potential at the point because of outside electric field E.
(ii) Potential Energy of an arrangement of two charges in an outer field
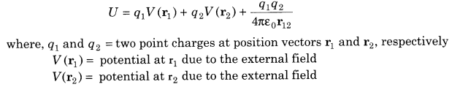
18.Likely vitality of a dipole in a uniform electric field E is given by
Expected vitality = – p .E
- Electrostatic Shielding The cycle which includes the creation of a locale liberated from any electric field is known as electrostatic protecting.
It occurs because of the way that no electric field exist inside a charged empty transmitter. Potential inside a shell is consistent. Thusly we can likewise infer that the field inside the shell (empty conductor) will be zero.