Body Fluids and Circulation: Class 11 Biology NCERT Chapter 18

Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 – Body Fluids and Circulation
In chapter 17 of NCERT class 11 Biology: Breathing and Exchange of gases, You learnt about the profound jump into the respiratory arrangement of the human framework. In this chapter: Body Fluids and Circulation, you will study about the part of body fluids and circulation will illuminate different fascinating ideas and realities about the equivalent.
It covers subjects of blood, lymph, circulation, and that’s only the tip of the iceberg. From that point onward, this section will assist you with finding out about the different issues which the circulatory framework needs to confront. Understudies definitely realize that every living creature require proficient components to move substances starting with one cell then onto the next. The body fluids and circulation class 11 notes simply explain this idea further.
Quick Revision Notes
In addition, it likewise explains the sythesis of blood. Therefore, you will get acquainted with the properties of lymph. The section likewise clarifies cautiously the instrument of circulation of blood. You can find out about the way pour organic fluids assume an incredible job. They help in keeping up the soundness of our body by continually performing exercises. In this way, body fluids and circulation class 11 notes will be valuable in seeing every one of these complexities and the sky is the limit from there.
Sub-points secured under Body Fluids and Circulation –
Blood–Students will find out about the life saver known as blood in this segment notwithstanding its significance.
Lymph–You will consider the huge arrangement of the lymphatic framework which is basic for the working of body.
Circulatory Pathways–Through this section, one will handily consider the circulatory pathways and their working in different living beings.
Twofold Circulation–It will examine the specific component present in winged creatures and well evolved creatures are known as the twofold circulation.
Issues of Circulatory System–This area illuminates the issues of the circulatory framework like respiratory failure and hypertension.
Quick revision notes
What exactly is blood?
Blood is an uncommon liquid that is really a connective tissue. We can consider it a vehicle fluid which is siphoned by the heart to various pieces of the body, after which it returns again to the heart. This is a procedure that happens constantly in your body, till your pulses. The cells of the body are profoundly defenseless and they need a consistent gracefully of blood. On the off chance that its stream stops, demise can happen in no time
It consists of the following components:
- Plasma ( fluid matrix)
- Blood cells
- The complex working of blood
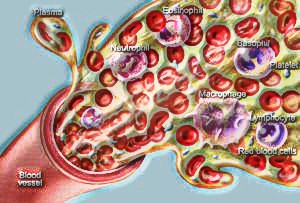
In people, the job of blood is noteworthy and it has an exceptionally mind boggling working structure. Its circulation helps in keeping up its consistency in the piece. Circulation is a procedure through which blood ventures all around the body, to various organs through particular blood vessels.
At some random time, contingent upon the organ from which blood is moving in or moving out, it’s setup changes. Obviously, the fundamental segments stay same. Be that as it may, the substance of the plasma changes.
Hence when blood goes to the lungs, it takes in oxygen and gives out carbon dioxide that is got from the tissues. In the digestive organs, food gets into the bloodstream, after ingestion, which at that point is shipped to different cells in various pieces of the body. Indeed, even the waste items are moved to the dispensing with organs through blood. The plasma additionally conveys the concoction couriers, the hormones to the objective organs.
Hence, there is a reasonable piece of reusing additionally that occurs. Take, for instance, the iron that is delivered because of the demolition of old RBC’s is reclaimed to the locales of new RBC creation and utilized by and by. At some random time, there ought to be a suitable degree of centralization of the various parts. There is an exceptionally powerful administrative instrument that guarantees this occurs.
Main Components of Blood
Plasma
It is a reasonable, somewhat clingy, yellowish hued fluid that contains the broke down proteins, mineral particles, glucose, hormones, carbon dioxide, including the blood cells. Around 90% of the plasma is comprised of water and around 6 % of it establishes the proteins. Egg whites is the fundamental protein in the plasma, which controls the osmotic blood pressure. 55% of the blood liquid is comprised of plasma.
Blood Cells
These constitute the other half, around 45%. There are three types of cells, namely:
- Erythrocytes or Red Blood cells ( RBC)
- Leucocytes or White Blood Cells ( WBC)
- Thrombocytes or Platelets
Erythrocytes – They structure around 40%-45% of its volume. They are produced from the bone marrow at an amazing pace of four to five billion cells for every hour. The life expectancy of these cells is 120 days. The RBCs are decimated in the organ called spleen, which is additionally called as the memorial park of RBC. These cells are red in shading, because of the nearness of hemoglobin, which is an iron-containing complex protein.
Leucocytes – They represent 1 % of the all out volume, however have a significant task to carry out. They help in battling infections and assault the unfamiliar bodies in the blood. These cells are lackluster as they don’t have hemoglobin. They are additionally continually created from the bone marrow.
Thrombocytes – These are cell parts that are delivered from the particular cells of the bone marrow. Their job is exceptionally huge. They are answerable for controlling draining or in thickening of blood.
Fast Facts
- It is a fluid connective tissue.
- It has two main components –that is, The fluid Plasma and the blood cells.
- RBCs – Number ranges between 4 millions and 6 million per cubic mm.
- WBCs – Number ranges between 4,500 and 11,000 per cubic millimetre.
- Platelets – 150,000 to 400,000 per cubic millimetre.
- The spleen is the graveyard of RBCs.
- It is red in colour due to the presence of haemoglobin.
- RBCs are without a nucleus and are biconcave in shape.
- WBCs are nucleated.
- Plasma has 90% water and around 6 % of proteins.
- The lifespan of RBCs is 120 days.
Questions
Q: What are the significant parts of blood?
Ans: Blood is comprised of two fundamental segments – Plasma and Blood cells. Plasma is a straw-shaded thick liquid which is 90% water and has numerous proteins in it. It likewise has mineral particles, glucose, hormones, carbon dioxide. It compensates for 55 % of the blood. The other 55% of blood is made up of blood cells. Therefor, these cells are of three kinds: Erythrocytes (RBC), Leucocytes (WBC) and Thrombocytes.
Q: Write a couple of lines on leucocytes.
Ans: Leucocytes are likewise called WBC’s. They are without any shading and don’t have hemoglobin. They are nucleated cells. Despite the fact that they represent just 1% of the volume, they have a significant task to carry out in being sound and battling infections. Hence, there are two fundamental sorts of WBCs – Agranulocytes and granulocytes. Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are the various kinds of granulocytes. Lymphocytes and monocytes are agranulocytes.

