Biomolecules: Class 11 Biology NCERT Chapter 9

Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules
In the previous chapter 8: Cell The Unit of Life, you studied that a cell is a structure that contains organelles that provide necessary functions to sustain itself. However, not all cells are the same. In this chapter: Biomolecules, you will study that our bodies are comprised of different of these complex biomolecules, for example, proteins, carbohydrates, and so forth. Let us become familiar with these in some detail.
One of the most marvelous realities is that every single living thing is basically comprised of non-living atoms and molecules. In chemistry, we endeavor to become familiar with these molecules that are named biomolecules.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 arrangements with Biomolecules. As a matter of first importance, Biomolecule alludes to a molecule that is produced by a living organism. Biomolecules incorporate lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. Moreover, they comprise of large macromolecules and small molecules. This section positively clarifies the idea of Biomolecules in detail. Additionally, students will figure out how to investigate chemical composition.
The section of Biomolecules in Class eleventh Biology serves of great importance. It acquaints students with molecules that are available in living organisms. Consequently, this part will assist you in finding out about a wide scope of sizes and structures. Accordingly, through biomolecules class 11 notes you will have the option to concentrate in insight regarding these things. It will help students understanding the associations of living creatures in a reasonable and brief way.
Quick revision notes
Biomacromolecules
Biomolecules or biological molecules are substances that are produced by the cells of the body and are found in living organisms. Biomolecules are broadly classified into two categories depending on their size:
- Biomicromolecules
- Biomacromolecules
Biomacromolecules are biomolecules having a size of 800 to 1000 daltons, large molecular weights, and complex structures. They are biological polymers of various simple or monomeric units. Instances of Biomacromolecules are Proteins, Nucleic Acids(DNA and RNA), Carbohydrates, and lipids.
Biomacromolecules in detail:
- Proteins:
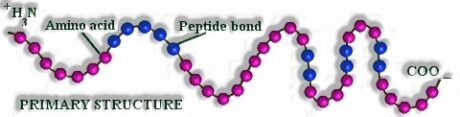
They are said to establish the majority of biomolecules in a cell. Simpler unit is known as amino acids make up these biological polymers. They are connected together by covalent bonds known as peptide bonds. There are 21 unique kinds of amino acids. Proteins are answerable for some capacities in the body. Subsequently, they are classified into various sorts dependent on their capacity for example structural proteins, enzyme proteins, transport proteins, and so on. Proteins have a complex structure that partitions into the Primary structure, Secondary structure, and tertiary structure.
- Nucleic Acids:
Smaller monomeric units that are known as nucleotides form nucleic acids. Nucleic acids manage different functions in the body, for example, growth, reproduction, and metabolism. These are parts which form the qualities of a person that is answerable for heredity. There are basically two kinds of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid comprises nucleotides comprised of four nitrogen bases to be specific adenine, guanine, thiamine, and cytosine. Though adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil( instead of thiamine) make up RNA or ribonucleic acid.
- Carbohydrates:
These are biomolecules that fundamentally contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Another name for them is sugars. Carbohydrates are classified into various classes relying upon the number of monomer units present in them, for example, monosaccharides(single monomer unit), disaccharides( two monomer units), polysaccharides(multiple monomer units). Monosaccharides have different names e.g glucose, fructose. Glucose is the vitality currency of the cells in creatures and fructose is in plants. These sugars contain an aldehyde group or a keto group and the bond between these groups and an alcoholic group of another monomer unit is known as a glycoside bond or linkage. Polysaccharides are basically of two sorts: structural and food storage.
- Lipids:
Lipids are like carbohydrates in that they are comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Be that as it may, they constitute an extremely heterogeneous group of substances. In contrast to carbohydrates, on hydrolysis, lipids yield glycerol and fatty acids. The fatty acids are of two kinds: unsaturated and immersed fatty acids and every one of them end with a carboxylic acid group. Lipids are likewise found in fats, oils, hormones, and different structures, for example, the cell layer. A complex form of lipids which is stored in the body as fat tissue is known as fatty substances Lipids are supposed to be ‘hydrophobic’ and are not miscible in water in contrast to the next biomacromolecules which are ‘hydrophilic’. Therefore, we can sum up to state that lipids function as vitality storage molecules, chemical couriers, and structural components of cells.
- Sub-topics secured under Biomolecules
- Biomacromolecules–This section will show students the molecules which the cells produce in our body.
- Bond connecting Monomers–Through this part, students will find out about the smaller units present in macromolecules known as monomers.
- Enzymes–You will find out about the proteins that living organisms produce make metabolic and chemical reactions in our body.
- Metabolic Basis For Living–It will talk about the manner in which our bodies convert the food we eat into vitality in order to deliver power.
- Nucleic Acids–Students will find out about the biomolecules which are building squares of an organism known as nucleic acid.
- Polysaccharides–The complex biomacromolecules comprised of chains of monosaccharides known as polysaccharides.
- Proteins–The complex biomolecules comprised of smaller units called amino acids named as proteins are instructed here.
Questions
Q: Which is the organic compound found in many cells?
Water
Glucose
Oxygen
Sodium Chloride
Solution: The correct answer is option “b”. Glucose is a monomer which is formed of six carbon atoms.

